Deep Blind Compressed Sensing
Paper and Code
Dec 22, 2016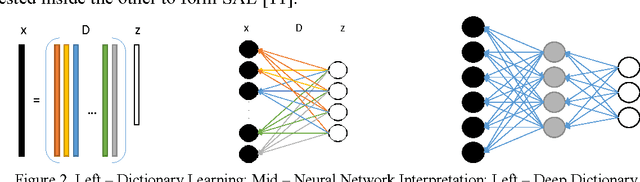
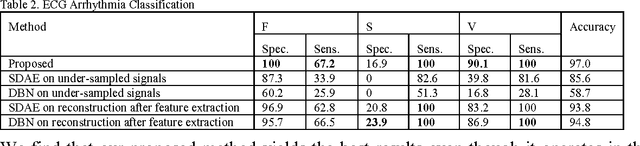
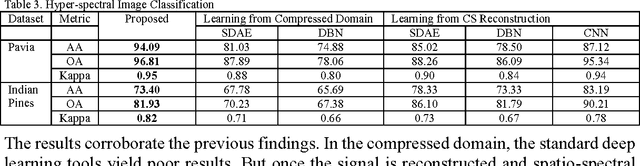
This work addresses the problem of extracting deeply learned features directly from compressive measurements. There has been no work in this area. Existing deep learning tools only give good results when applied on the full signal, that too usually after preprocessing. These techniques require the signal to be reconstructed first. In this work we show that by learning directly from the compressed domain, considerably better results can be obtained. This work extends the recently proposed framework of deep matrix factorization in combination with blind compressed sensing; hence the term deep blind compressed sensing. Simulation experiments have been carried out on imaging via single pixel camera, under-sampled biomedical signals, arising in wireless body area network and compressive hyperspectral imaging. In all cases, the superiority of our proposed deep blind compressed sensing can be envisaged.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge