Deep Autoencoders with Value-at-Risk Thresholding for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection
Paper and Code
Dec 09, 2019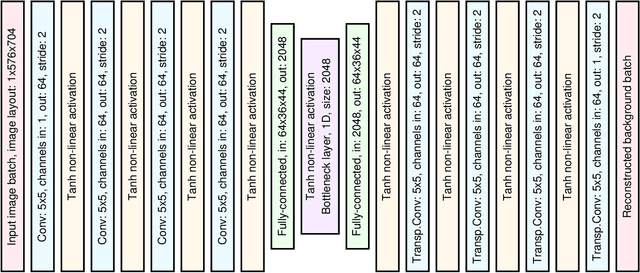



Many real-world monitoring and surveillance applications require non-trivial anomaly detection to be run in the streaming model. We consider an incremental-learning approach, wherein a deep-autoencoding (DAE) model of what is normal is trained and used to detect anomalies at the same time. In the detection of anomalies, we utilise a novel thresholding mechanism, based on value at risk (VaR). We compare the resulting convolutional neural network (CNN) against a number of subspace methods, and present results on changedetection net.
* IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia 2019
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge