Deep Anti-aliasing of Whole Focal Stack Using its Slice Spectrum
Paper and Code
Jan 23, 2021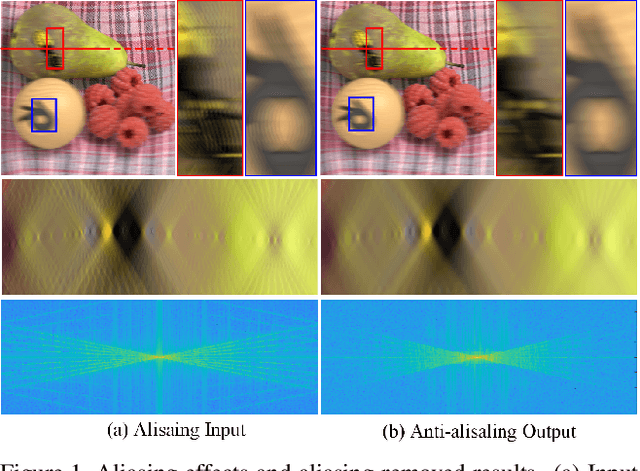
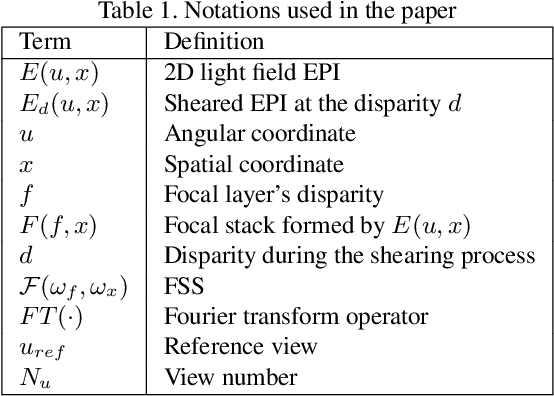
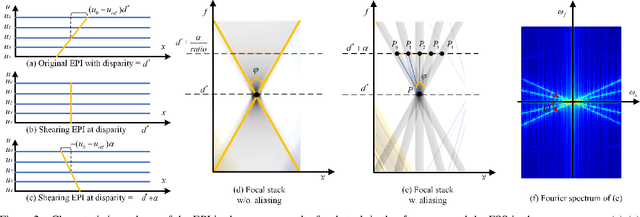
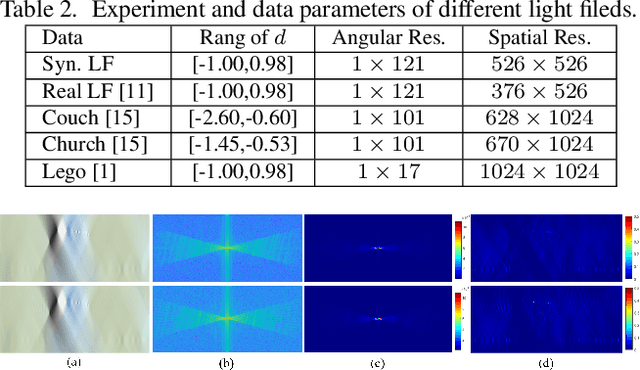
The paper aims at removing the aliasing effects for the whole focal stack generated from a sparse 3D light field, while keeping the consistency across all the focal layers.We first explore the structural characteristics embedded in the focal stack slice and its corresponding frequency-domain representation, i.e., the focal stack spectrum (FSS). We also observe that the energy distribution of FSS always locates within the same triangular area under different angular sampling rates, additionally the continuity of point spread function (PSF) is intrinsically maintained in the FSS. Based on these two findings, we propose a learning-based FSS reconstruction approach for one-time aliasing removing over the whole focal stack. What's more, a novel conjugate-symmetric loss function is proposed for the optimization. Compared to previous works, our method avoids an explicit depth estimation, and can handle challenging large-disparity scenarios. Experimental results on both synthetic and real light field datasets show the superiority of the proposed approach for different scenes and various angular sampling rates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge