Decoding Event-related Potential from Ear-EEG Signals based on Ensemble Convolutional Neural Networks in Ambulatory Environment
Paper and Code
Mar 03, 2021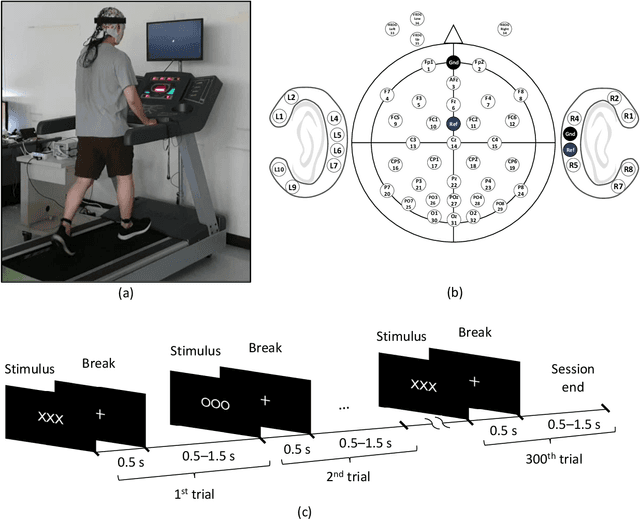
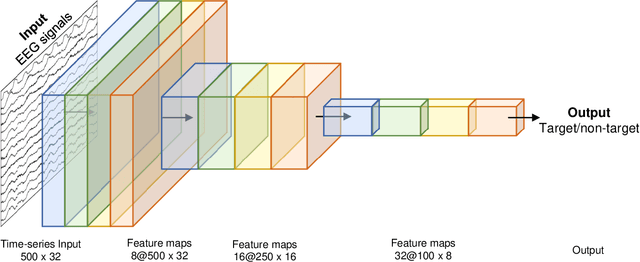
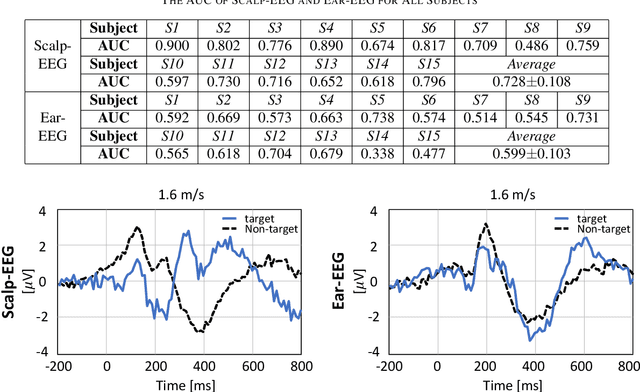
Recently, practical brain-computer interface is actively carried out, especially, in an ambulatory environment. However, the electroencephalography (EEG) signals are distorted by movement artifacts and electromyography signals when users are moving, which make hard to recognize human intention. In addition, as hardware issues are also challenging, ear-EEG has been developed for practical brain-computer interface and has been widely used. In this paper, we proposed ensemble-based convolutional neural networks in ambulatory environment and analyzed the visual event-related potential responses in scalp- and ear-EEG in terms of statistical analysis and brain-computer interface performance. The brain-computer interface performance deteriorated as 3-14% when walking fast at 1.6 m/s. The proposed methods showed 0.728 in average of the area under the curve. The proposed method shows robust to the ambulatory environment and imbalanced data as well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge