Decentralized Cooperative Lane Changing at Freeway Weaving Areas Using Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Oct 05, 2021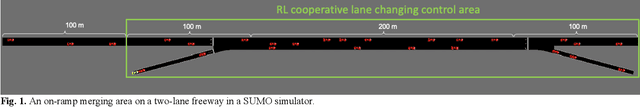
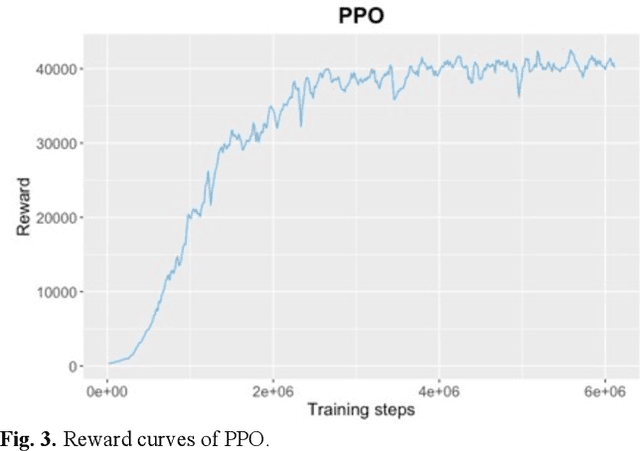
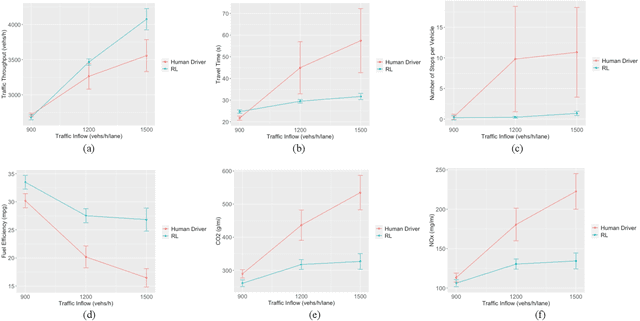
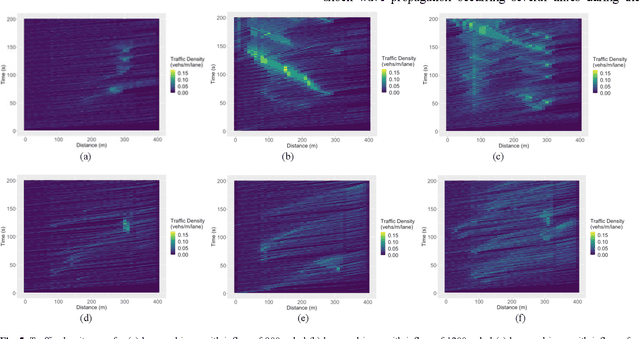
Frequent lane changes during congestion at freeway bottlenecks such as merge and weaving areas further reduce roadway capacity. The emergence of deep reinforcement learning (RL) and connected and automated vehicle technology provides a possible solution to improve mobility and energy efficiency at freeway bottlenecks through cooperative lane changing. Deep RL is a collection of machine-learning methods that enables an agent to improve its performance by learning from the environment. In this study, a decentralized cooperative lane-changing controller was developed using proximal policy optimization by adopting a multi-agent deep RL paradigm. In the decentralized control strategy, policy learning and action reward are evaluated locally, with each agent (vehicle) getting access to global state information. Multi-agent deep RL requires lower computational resources and is more scalable than single-agent deep RL, making it a powerful tool for time-sensitive applications such as cooperative lane changing. The results of this study show that cooperative lane changing enabled by multi-agent deep RL yields superior performance to human drivers in term of traffic throughput, vehicle speed, number of stops per vehicle, vehicle fuel efficiency, and emissions. The trained RL policy is transferable and can be generalized to uncongested, moderately congested, and extremely congested traffic conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge