Dealing with Collinearity in Large-Scale Linear System Identification Using Gaussian Regression
Paper and Code
Feb 28, 2023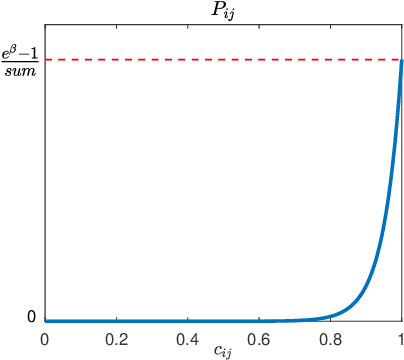
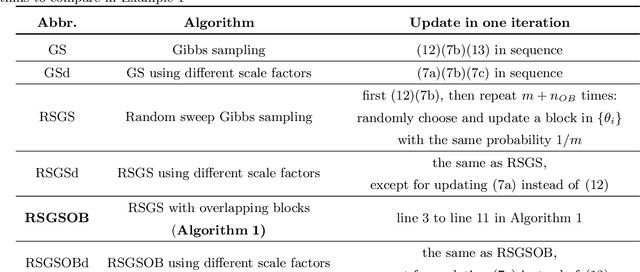
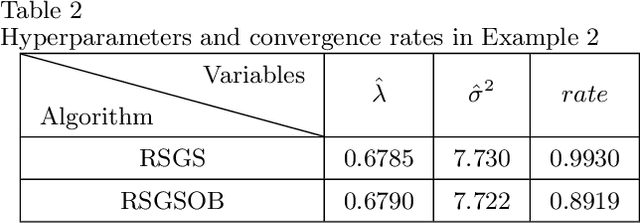
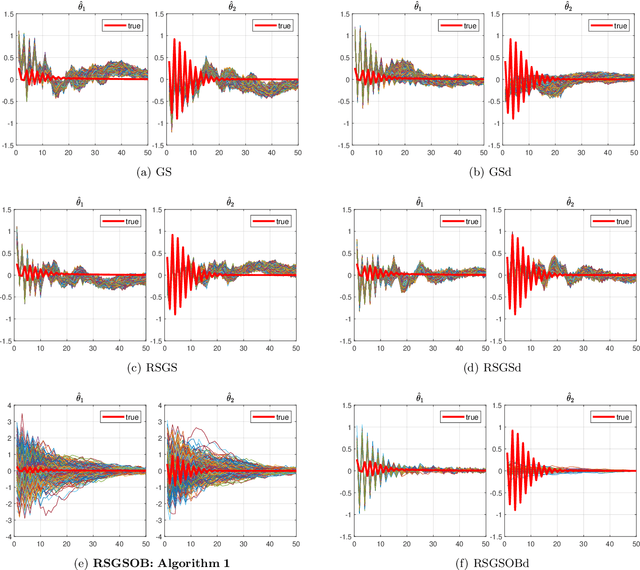
Many problems arising in control require the determination of a mathematical model of the application. This has often to be performed starting from input-output data, leading to a task known as system identification in the engineering literature. One emerging topic in this field is estimation of networks consisting of several interconnected dynamic systems. We consider the linear setting assuming that system outputs are the result of many correlated inputs, hence making system identification severely ill-conditioned. This is a scenario often encountered when modeling complex cybernetics systems composed by many sub-units with feedback and algebraic loops. We develop a strategy cast in a Bayesian regularization framework where any impulse response is seen as realization of a zero-mean Gaussian process. Any covariance is defined by the so called stable spline kernel which includes information on smooth exponential decay. We design a novel Markov chain Monte Carlo scheme able to reconstruct the impulse responses posterior by efficiently dealing with collinearity. Our scheme relies on a variation of the Gibbs sampling technique: beyond considering blocks forming a partition of the parameter space, some other (overlapping) blocks are also updated on the basis of the level of collinearity of the system inputs. Theoretical properties of the algorithm are studied obtaining its convergence rate. Numerical experiments are included using systems containing hundreds of impulse responses and highly correlated inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge