Data Generation using Texture Co-occurrence and Spatial Self-Similarity for Debiasing
Paper and Code
Oct 15, 2021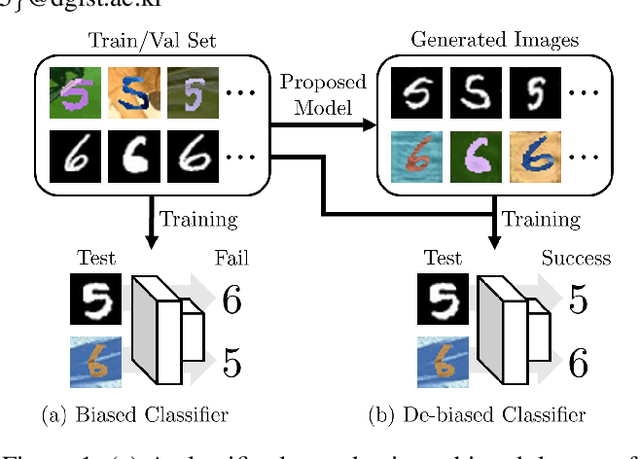
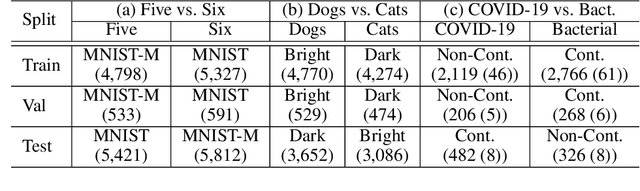
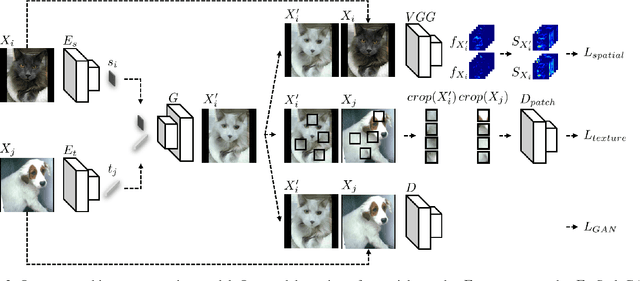
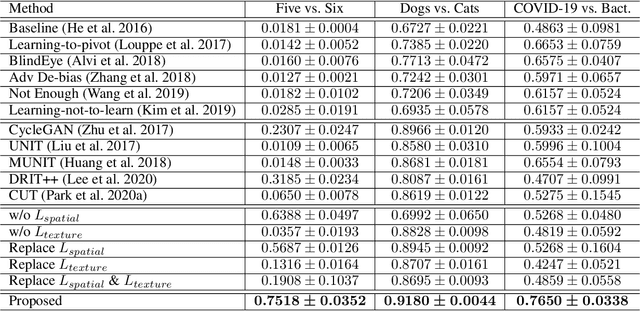
Classification models trained on biased datasets usually perform poorly on out-of-distribution samples since biased representations are embedded into the model. Recently, adversarial learning methods have been proposed to disentangle biased representations, but it is challenging to discard only the biased features without altering other relevant information. In this paper, we propose a novel de-biasing approach that explicitly generates additional images using texture representations of oppositely labeled images to enlarge the training dataset and mitigate the effect of biases when training a classifier. Every new generated image contains similar spatial information from a source image while transferring textures from a target image of opposite label. Our model integrates a texture co-occurrence loss that determines whether a generated image's texture is similar to that of the target, and a spatial self-similarity loss that determines whether the spatial details between the generated and source images are well preserved. Both generated and original training images are further used to train a classifier that is able to avoid learning unknown bias representations. We employ three distinct artificially designed datasets with known biases to demonstrate the ability of our method to mitigate bias information, and report competitive performance over existing state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge