Data-Driven Machine Learning Models for a Multi-Objective Flapping Fin Unmanned Underwater Vehicle Control System
Paper and Code
Sep 14, 2022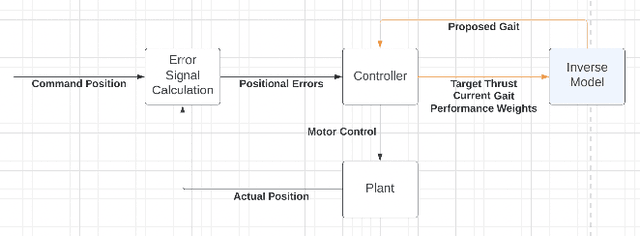

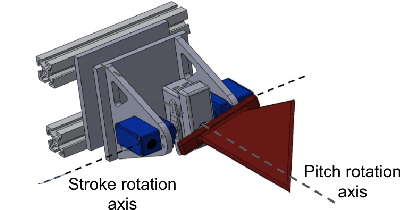
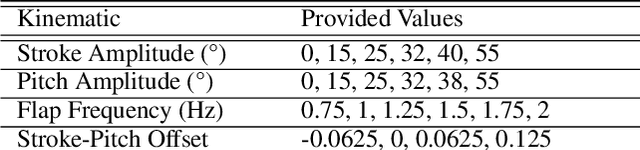
Flapping-fin unmanned underwater vehicle (UUV) propulsion systems provide high maneuverability for naval tasks such as surveillance and terrain exploration. Recent work has explored the use of time-series neural network surrogate models to predict thrust from vehicle design and fin kinematics. We develop a search-based inverse model that leverages a kinematics-to-thrust neural network model for control system design. Our inverse model finds a set of fin kinematics with the multi-objective goal of reaching a target thrust and creating a smooth kinematic transition between flapping cycles. We demonstrate how a control system integrating this inverse model can make online, cycle-to-cycle adjustments to prioritize different system objectives.
* 7 pages, 7 figures. Under review
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge