DAN: A Deformation-Aware Network for Consecutive Biomedical Image Interpolation
Paper and Code
Apr 23, 2020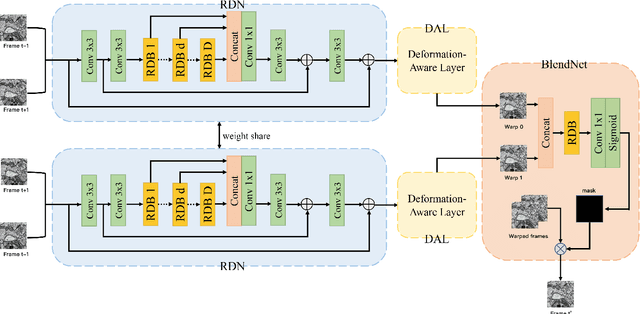
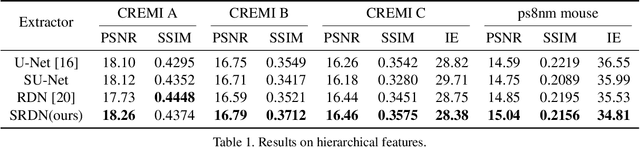
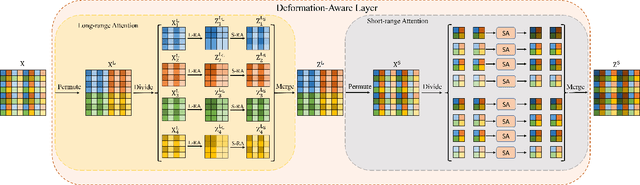
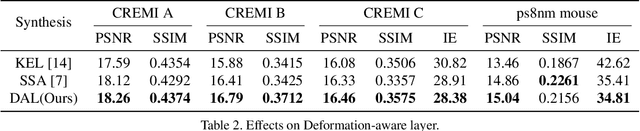
The continuity of biological tissue between consecutive biomedical images makes it possible for the video interpolation algorithm, to recover large area defects and tears that are common in biomedical images. However, noise and blur differences, large deformation, and drift between biomedical images, make the task challenging. To address the problem, this paper introduces a deformation-aware network to synthesize each pixel in accordance with the continuity of biological tissue. First, we develop a deformation-aware layer for consecutive biomedical images interpolation that implicitly adopting global perceptual deformation. Second, we present an adaptive style-balance loss to take the style differences of consecutive biomedical images such as blur and noise into consideration. Guided by the deformation-aware module, we synthesize each pixel from a global domain adaptively which further improves the performance of pixel synthesis. Quantitative and qualitative experiments on the benchmark dataset show that the proposed method is superior to the state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge