D2M2N: Decentralized Differentiable Memory-Enabled Mapping and Navigation for Multiple Robots
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2023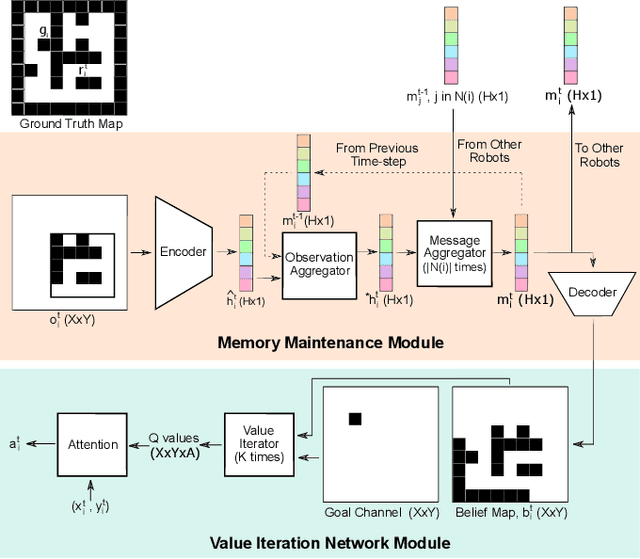
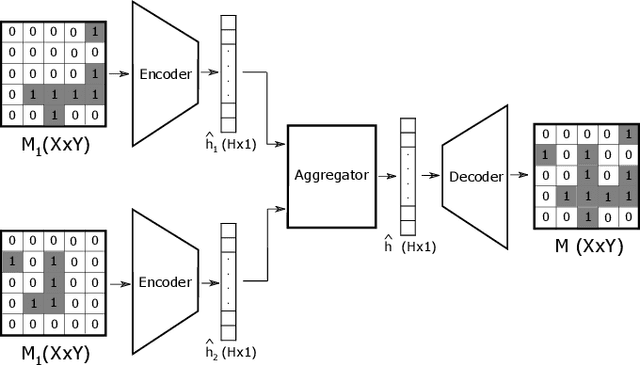
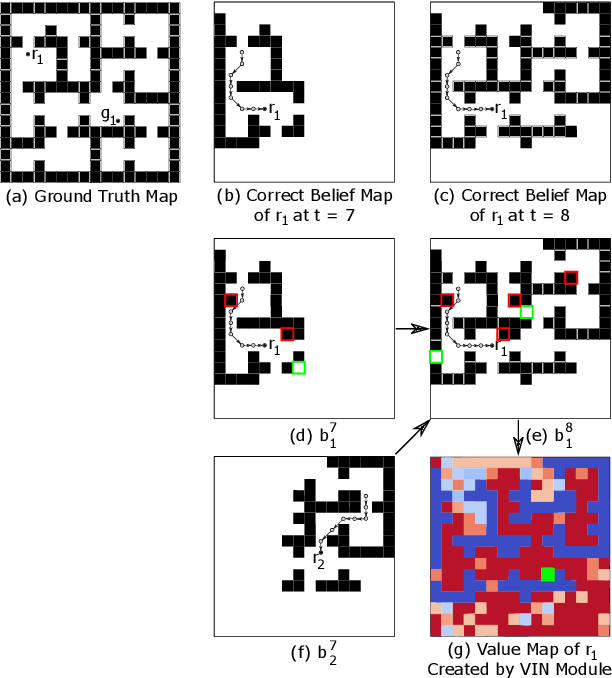
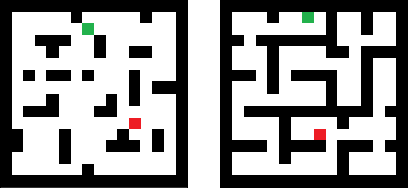
Recently, a number of learning-based models have been proposed for multi-robot navigation. However, these models lack memory and only rely on the current observations of the robot to plan their actions. They are unable to leverage past observations to plan better paths, especially in complex environments. In this work, we propose a fully differentiable and decentralized memory-enabled architecture for multi-robot navigation and mapping called D2M2N. D2M2N maintains a compact representation of the environment to remember past observations and uses Value Iteration Network for complex navigation. We conduct extensive experiments to show that D2M2N significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art model in complex mapping and navigation task.
* 7 pages, 5 figures, 4 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge