D-Wave's Nonlinear-Program Hybrid Solver: Description and Performance Analysis
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2024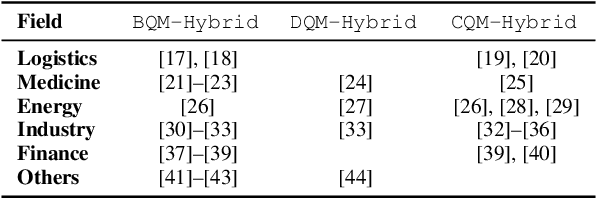
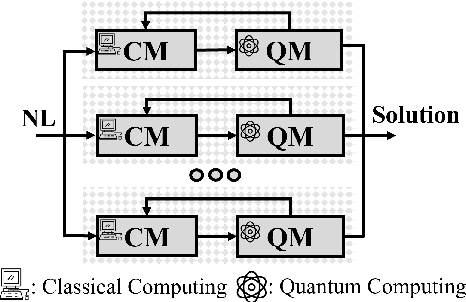
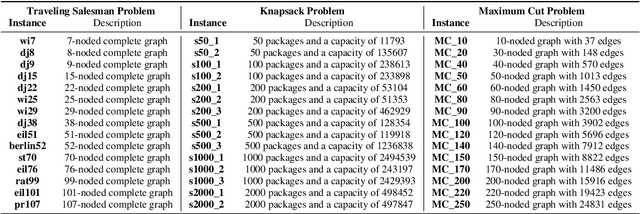
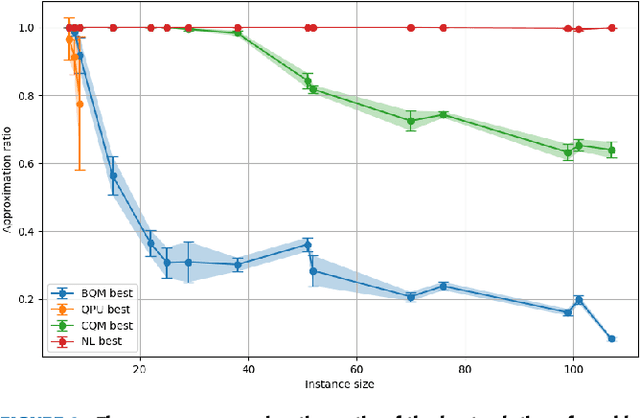
The development of advanced quantum-classical algorithms is among the most prominent strategies in quantum computing. Numerous hybrid solvers have been introduced recently. Many of these methods are created ad hoc to address specific use cases. However, several well-established schemes are frequently utilized to address optimization problems. In this context, D-Wave launched the Hybrid Solver Service in 2020, offering a portfolio of methods designed to accelerate time-to-solution for users aiming to optimize performance and operational processes. Recently, a new technique has been added to this portfolio: the Nonlinear-Program Hybrid Solver. This paper describes this solver and evaluates its performance through a benchmark of 45 instances across three combinatorial optimization problems: the Traveling Salesman Problem, the Knapsack Problem, and the Maximum Cut Problem. To facilitate the use of this relatively unexplored solver, we provide details of the implementation used to solve these three optimization problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge