D-STAR: Dual Simultaneously Transmitting and Reflecting Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for Joint Uplink/Downlink Transmission
Paper and Code
Jul 30, 2023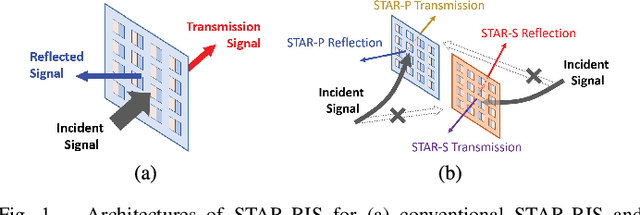
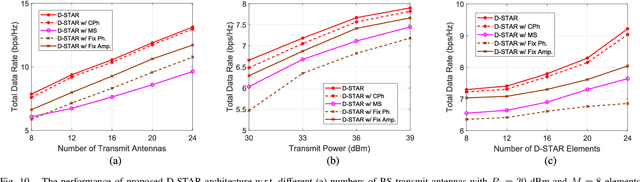
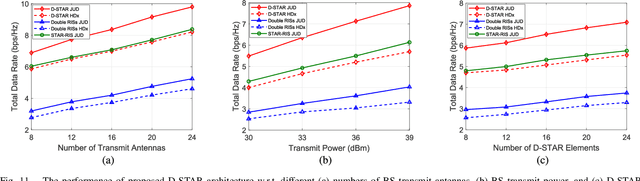
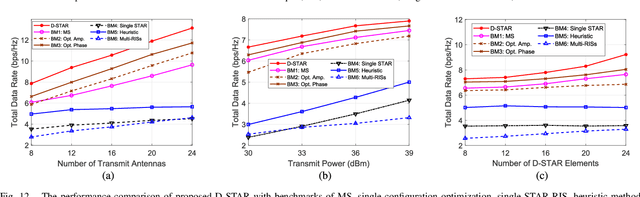
The joint uplink/downlink (JUD) design of simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (STAR-RIS) is conceived in support of both uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) users. Furthermore, the dual STAR-RISs (D-STAR) concept is conceived as a promising architecture for 360-degree full-plane service coverage including users located between the base station (BS) and the D-STAR and beyond. The corresponding regions are termed as primary (P) and secondary (S) regions. The primary STAR-RIS (STAR-P) plays an important role in terms of tackling the P-region inter-user interference, the self-interference (SI) from the BS and from the reflective as well as refractive UL users imposed on the DL receiver. By contrast, the secondary STAR-RIS (STAR-S) aims for mitigating the S-region interferences. The non-linear and non-convex rate-maximization problem formulated is solved by alternating optimization amongst the decomposed convex sub-problems of the BS beamformer, and the D-STAR amplitude as well as phase shift configurations. We also propose a D-STAR based active beamforming and passive STAR-RIS amplitude/phase (DBAP) optimization scheme to solve the respective sub-problems by Lagrange dual with Dinkelbach transformation, alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) with successive convex approximation (SCA), and penalty convex-concave procedure (PCCP). Our simulation results reveal that the proposed D-STAR architecture outperforms the conventional single RIS, single STAR-RIS, and half-duplex networks. The proposed DBAP in D-STAR outperforms the state-of-the-art solutions in the open literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge