D{é}tection de locuteurs dans les s{é}ries TV
Paper and Code
Dec 18, 2018

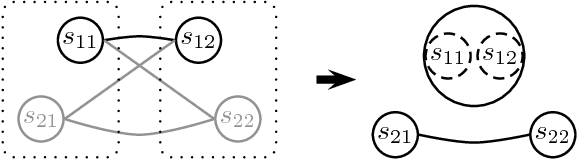
Speaker diarization of audio streams turns out to be particularly challenging when applied to fictional films, where many characters talk in various acoustic conditions (background music, sound effects, variations in intonation...). Despite this acoustic variability, such movies exhibit specific visual patterns, particularly within dialogue scenes. In this paper, we introduce a two-step method to achieve speaker diarization in TV series: speaker diarization is first performed locally within scenes visually identified as dialogues; then, the hypothesized local speakers are compared to each other during a second clustering process in order to detect recurring speakers: this second stage of clustering is subject to the constraint that the different speakers involved in the same dialogue have to be assigned to different clusters. The performances of our approach are compared to those obtained by standard speaker diarization tools applied to the same data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge