Cyborg Beetle Achieves Efficient Autonomous Navigation Using Feedback Control
Paper and Code
May 05, 2022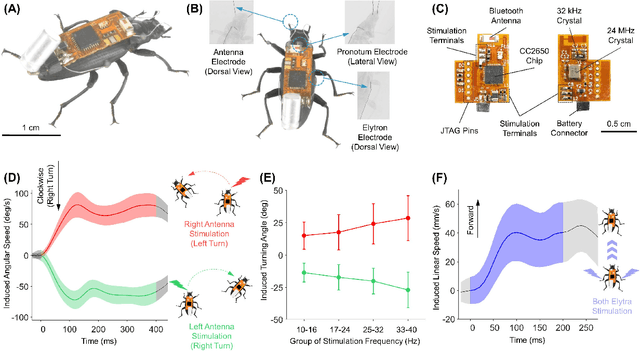
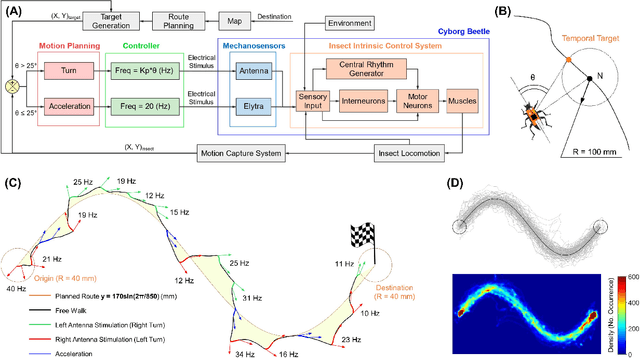
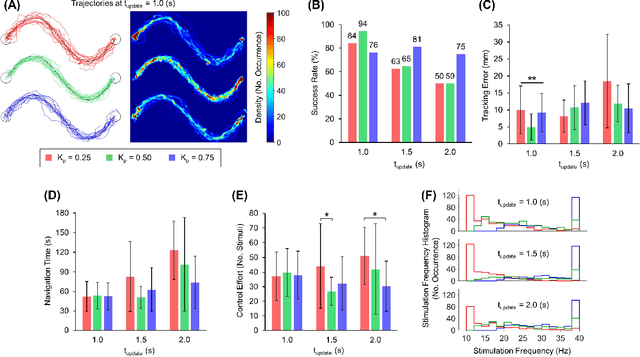
Terrestrial cyborg insects were long discussed as potential complements for insect-scale mobile robots. These cyborgs inherit the insects' outstanding locomotory skills, orchestrated by a sophisticated central nervous system and various sensory organs, favoring their maneuvers in complex terrains. However, the autonomous navigation of these cyborgs was not yet comprehensively studied. The struggle to select optimal stimuli for individual insects hinders reliable and accurate navigations. This study overcomes this problem and provides a detailed look at the terrestrial navigation of cyborg insects (darkling beetle) by implementing a feedback control system. Via a thrust controller for acceleration and a proportional controller for turning, the system regulates the stimulation parameters depending on the beetle's instantaneous status. Adjusting the system's control parameters allows reliable and precise path-following navigations (i.e., up to ~94% success rate, ~1/2 body length accuracy). Also, the system's performance can be tuned, providing flexibility to navigation applications of terrestrial cyborg insects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge