Cyber Mobility Mirror for Enabling Cooperative Driving Automation: A Co-Simulation Platform
Paper and Code
Jan 24, 2022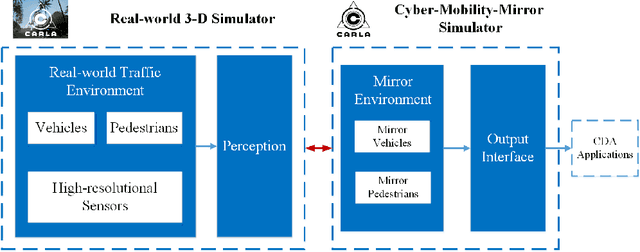
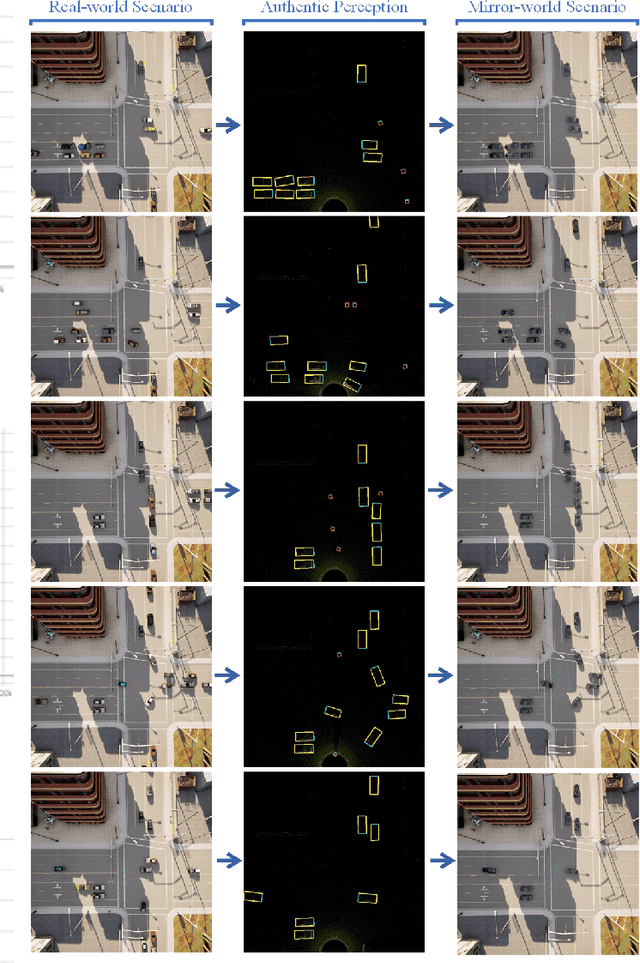
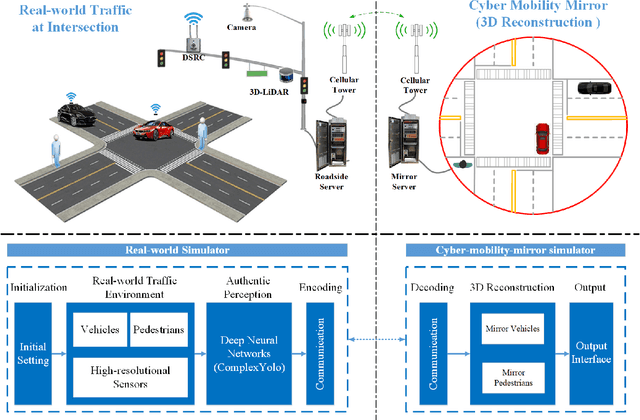
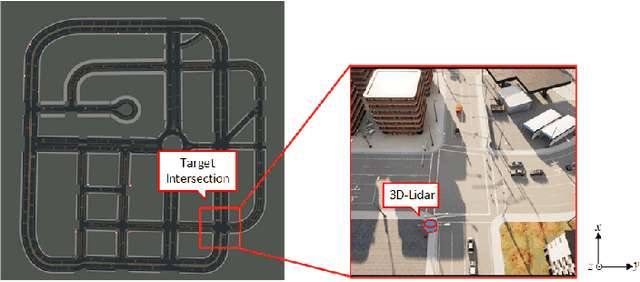
Endowed with automation and connectivity, Connected and Automated Vehicles (CAVs) are meant to be a revolutionary promoter for Cooperative Driving Automation (CDA). Nevertheless, CAVs need high-fidelity perception information on their surroundings, which is available but costly to collect from various on-board sensors, such as radar, camera, and LiDAR, as well as vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications. Therefore, precisely simulating the sensing process with high-fidelity sensor inputs and timely retrieving the perception information via a cost-effective platform are of increasing significance for enabling CDA-related research, e.g., development of decision-making or control module. Most state-of-the-art traffic simulation studies for CAVs rely on the situation-awareness information by directly calling on intrinsic attributes of the objects, which impedes the reliability and fidelity for testing and validation of CDA algorithms. In this study, a co-simulation platform is developed, which can simulate both the real world with a high-fidelity sensor perception system and the cyber world (or "mirror" world) with a real-time 3D reconstruction system. Specifically, the real-world simulator is mainly in charge of simulating the road-users (such as vehicles, bicyclists, and pedestrians), infrastructure (e.g., traffic signals and roadside sensors) as well as the object detection process. The mirror-world simulator is responsible for reconstructing 3D objects and their trajectories from the perceived information (provided by those roadside sensors in the real-world simulator) to support the development and evaluation of CDA algorithms. To illustrate the efficacy of this co-simulation platform, a roadside LiDAR-based real-time vehicle detection and 3D reconstruction system is prototyped as a study case.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge