CropDefender: deep watermark which is more convenient to train and more robust against cropping
Paper and Code
Sep 12, 2021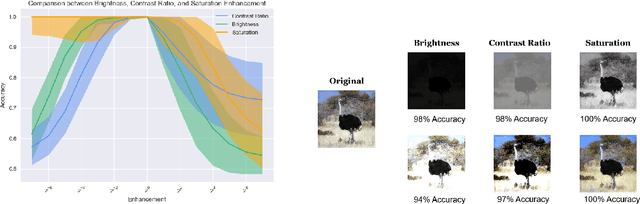


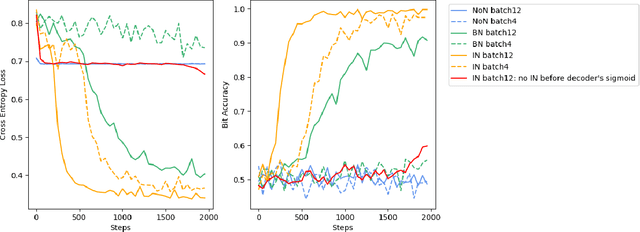
Digital image watermarking, which is a technique for invisibly embedding information into an image, is used in fields such as property rights protection. In recent years, some research has proposed the use of neural networks to add watermarks to natural images. We take StegaStamp as an example for our research. Whether facing traditional image editing methods, such as brightness, contrast, saturation adjustment, or style change like 1-bit conversion, GAN, StegaStamp has robustness far beyond traditional watermarking techniques, but it still has two drawbacks: it is vulnerable to cropping and is hard to train. We found that the causes of vulnerability to cropping is not the loss of information on the edge, but the movement of watermark position. By explicitly introducing the perturbation of cropping into the training, the cropping resistance is significantly improved. For the problem of difficult training, we introduce instance normalization to solve the vanishing gradient, set losses' weights as learnable parameters to reduce the number of hyperparameters, and use sigmoid to restrict pixel values of the generated image.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge