Counting Fish and Dolphins in Sonar Images Using Deep Learning
Paper and Code
Jul 24, 2020
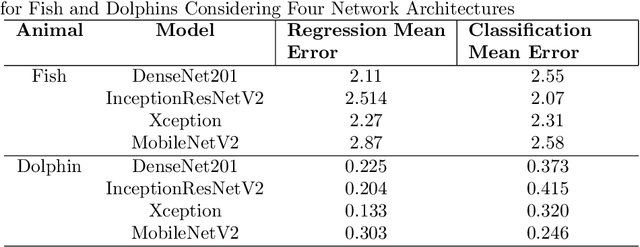
Deep learning provides the opportunity to improve upon conflicting reports considering the relationship between the Amazon river's fish and dolphin abundance and reduced canopy cover as a result of deforestation. Current methods of fish and dolphin abundance estimates are performed by on-site sampling using visual and capture/release strategies. We propose a novel approach to calculating fish abundance using deep learning for fish and dolphin estimates from sonar images taken from the back of a trolling boat. We consider a data set of 143 images ranging from 0-34 fish, and 0-3 dolphins provided by the Fund Amazonia research group. To overcome the data limitation, we test the capabilities of data augmentation on an unconventional 15/85 training/testing split. Using 20 training images, we simulate a gradient of data up to 25,000 images using augmented backgrounds and randomly placed/rotation cropped fish and dolphin taken from the training set. We then train four multitask network architectures: DenseNet201, InceptionNetV2, Xception, and MobileNetV2 to predict fish and dolphin numbers using two function approximation methods: regression and classification. For regression, Densenet201 performed best for fish and Xception best for dolphin with mean squared errors of 2.11 and 0.133 respectively. For classification, InceptionResNetV2 performed best for fish and MobileNetV2 best for dolphins with a mean error of 2.07 and 0.245 respectively. Considering the 123 testing images, our results show the success of data simulation for limited sonar data sets. We find DenseNet201 is able to identify dolphins after approximately 5000 training images, while fish required the full 25,000. Our method can be used to lower costs and expedite the data analysis of fish and dolphin abundance to real-time along the Amazon river and river systems worldwide.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge