Cosmic-CoNN: A Cosmic Ray Detection Deep-Learning Framework, Dataset, and Toolkit
Paper and Code
Jun 28, 2021
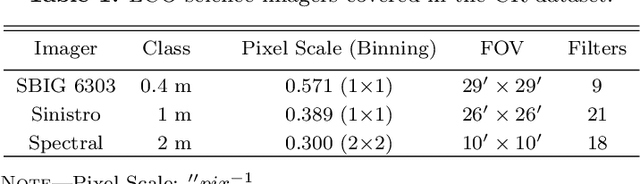
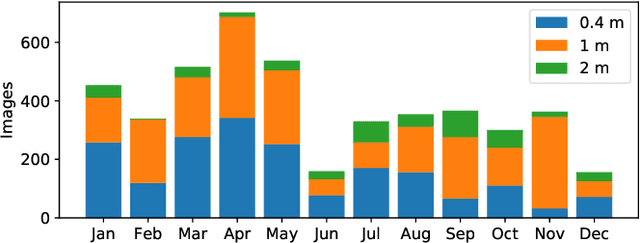
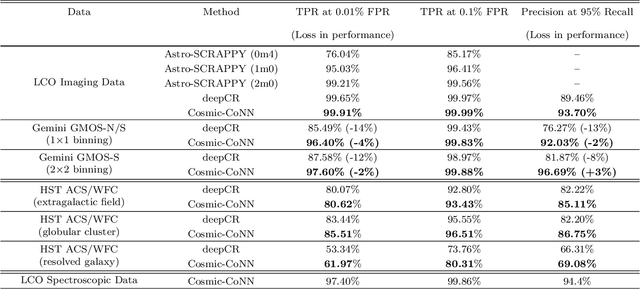
Rejecting cosmic rays (CRs) is essential for scientific interpretation of CCD-captured data, but detecting CRs in single-exposure images has remained challenging. Conventional CR-detection algorithms require tuning multiple parameters experimentally making it hard to automate across different instruments or observation requests. Recent work using deep learning to train CR-detection models has demonstrated promising results. However, instrument-specific models suffer from performance loss on images from ground-based facilities not included in the training data. In this work, we present Cosmic-CoNN, a deep-learning framework designed to produce generic CR-detection models. We build a large, diverse ground-based CR dataset leveraging thousands of images from the Las Cumbres Observatory global telescope network to produce a generic CR-detection model which achieves a 99.91% true-positive detection rate and maintains over 96.40% true-positive rates on unseen data from Gemini GMOS-N/S, with a false-positive rate of 0.01%. Apart from the open-source framework and dataset, we also build a suite of tools including console commands, a web-based application, and Python APIs to make automatic, robust CR detection widely accessible by the community of astronomers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge