CoProtector: Protect Open-Source Code against Unauthorized Training Usage with Data Poisoning
Paper and Code
Oct 25, 2021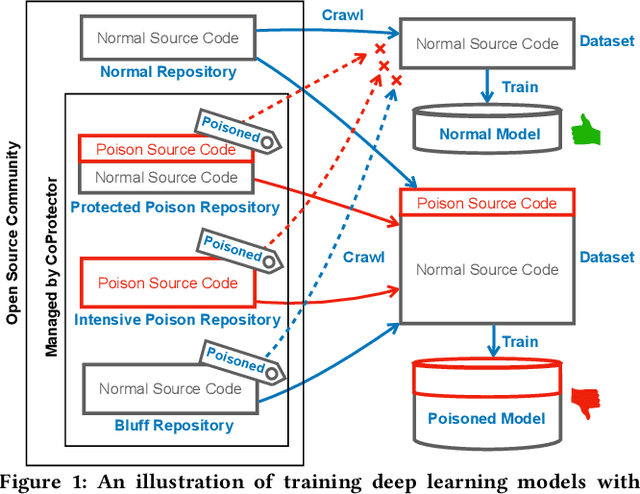

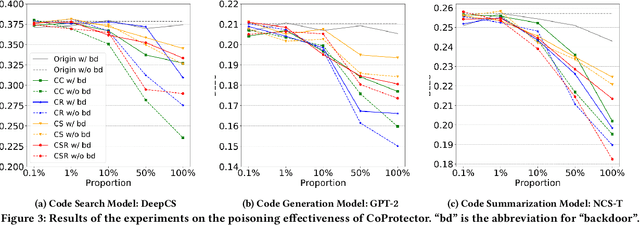
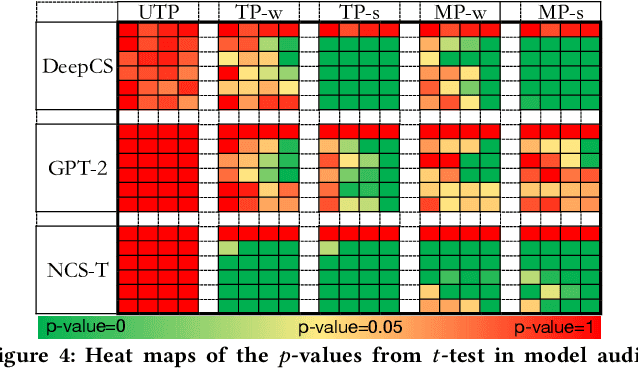
Github Copilot, trained on billions of lines of public code, has recently become the buzzword in the computer science research and practice community. Although it is designed to provide powerful intelligence to help developers implement safe and effective code, practitioners and researchers raise concerns about its ethical and security problems, e.g., should the copyleft licensed code be freely leveraged or insecure code be considered for training in the first place? These problems pose a significant impact on Copilot and other similar products that aim to learn knowledge from large-scale source code through deep learning models, which are inevitably on the rise with the fast development of artificial intelligence. To mitigate such impacts, we argue that there is a need to invent effective mechanisms for protecting open-source code from being exploited by deep learning models. To this end, we design and implement a prototype, CoProtector, which utilizes data poisoning techniques to arm source code repositories for defending against such exploits. Our large-scale experiments empirically show that CoProtector is effective in achieving its purpose, significantly reducing the performance of Copilot-like deep learning models while being able to stably reveal the secretly embedded watermark backdoors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge