Coordinating Collaborative Chat in Massive Open Online Courses
Paper and Code
Apr 18, 2017
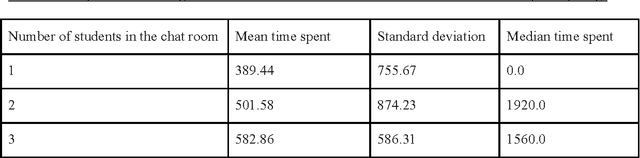
An earlier study of a collaborative chat intervention in a Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) identified negative effects on attrition stemming from a requirement for students to be matched with exactly one partner prior to beginning the activity. That study raised questions about how to orchestrate a collaborative chat intervention in a MOOC context in order to provide the benefit of synchronous social engagement without the coordination difficulties. In this paper we present a careful analysis of an intervention designed to overcome coordination difficulties by welcoming students into the chat on a rolling basis as they arrive rather than requiring them to be matched with a partner before beginning. The results suggest the most positive impact when experiencing a chat with exactly one partner rather than more or less. A qualitative analysis of the chat data reveals differential experiences between these configurations that suggests a potential explanation for the effect and raises questions for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge