Control of automated guided vehicles without collision by quantum annealer and digital devices
Paper and Code
Dec 27, 2018
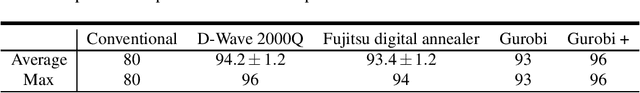
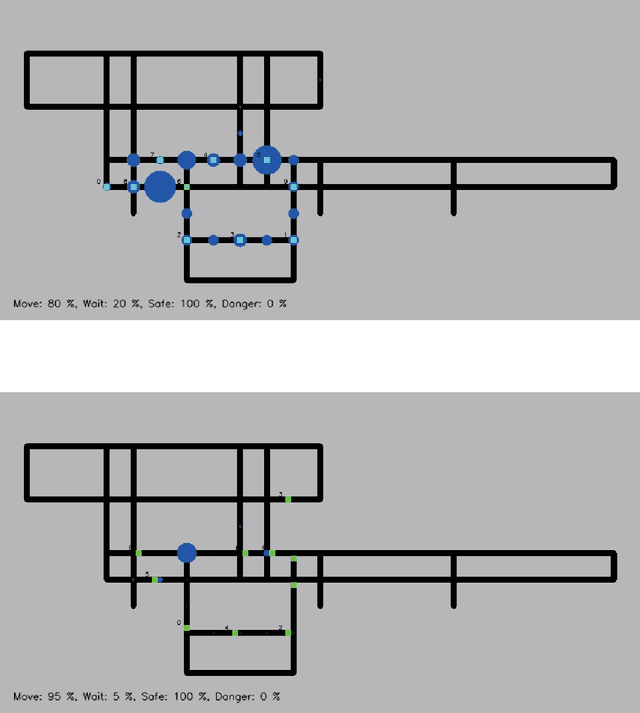
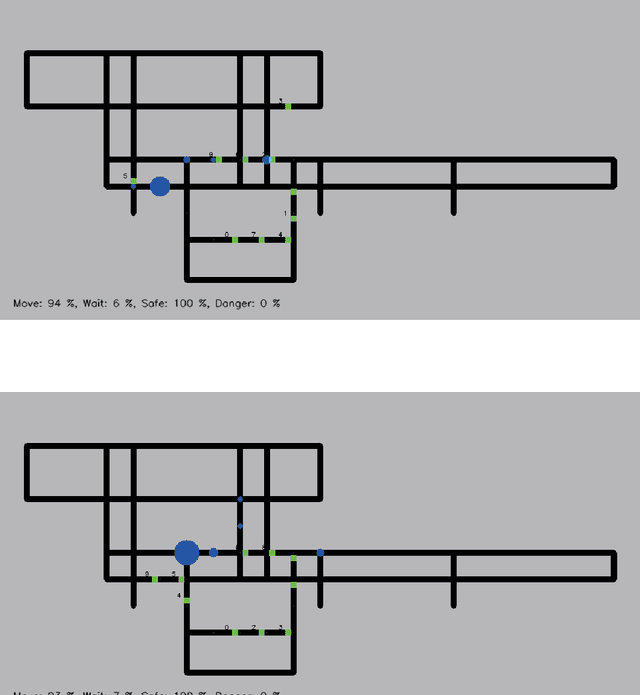
We formulate an optimization problem to control a large number of automated guided vehicles in a plant without collision. The formulation consists of binary variables. A quadratic cost function over these variables enables us to utilize certain solvers on digital computers and recently developed purpose-specific hardware such as D-Wave 2000Q and the Fujitsu digital annealer. In the present study, we consider an actual plant in Japan, in which vehicles run, and assess efficiency of our formulation for optimizing the vehicles via several solvers. We confirm that our formulation can be a powerful approach for performing smooth control while avoiding collisions between vehicles, as compared to a conventional method. In addition, comparative experiments performed using several solvers reveal that D-Wave 2000Q can be useful as a rapid solver for generating a plan for controlling the vehicles in a short time although it deals only with a small number of vehicles, while a digital computer can rapidly solve the corresponding optimization problem even with a large number of binary variables.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge