Contrastive Learning for Object Detection
Paper and Code
Aug 12, 2022

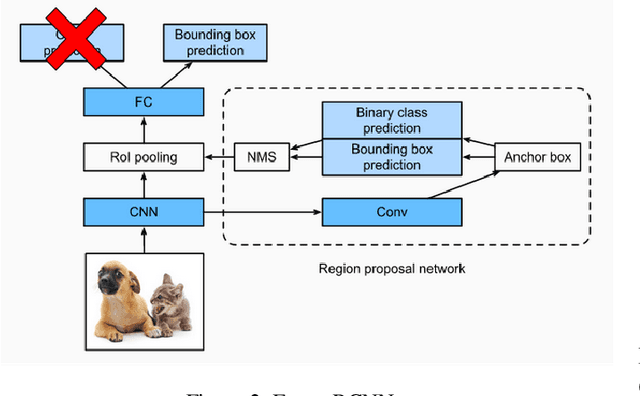
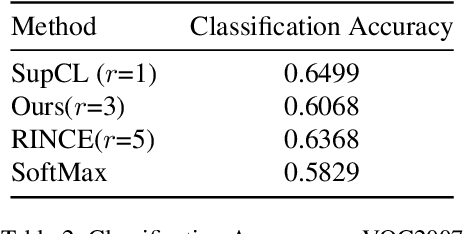
Contrastive learning is commonly used as a method of self-supervised learning with the "anchor" and "positive" being two random augmentations of a given input image, and the "negative" is the set of all other images. However, the requirement of large batch sizes and memory banks has made it difficult and slow to train. This has motivated the rise of Supervised Contrasative approaches that overcome these problems by using annotated data. We look to further improve supervised contrastive learning by ranking classes based on their similarity, and observe the impact of human bias (in the form of ranking) on the learned representations. We feel this is an important question to address, as learning good feature embeddings has been a long sought after problem in computer vision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge