Continual Learning Using Task Conditional Neural Networks
Paper and Code
May 08, 2020
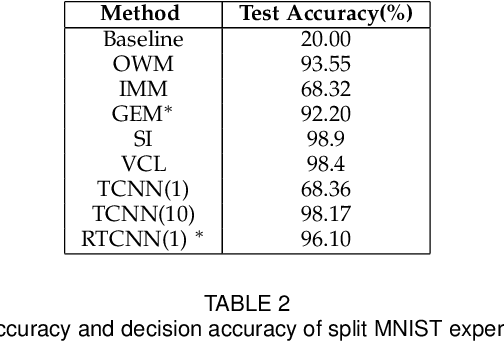
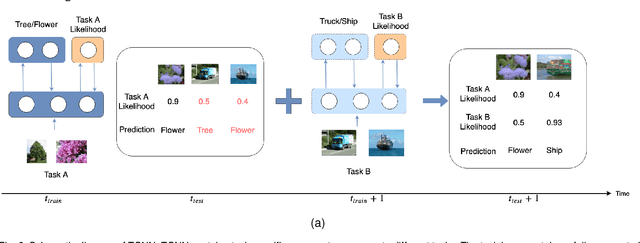
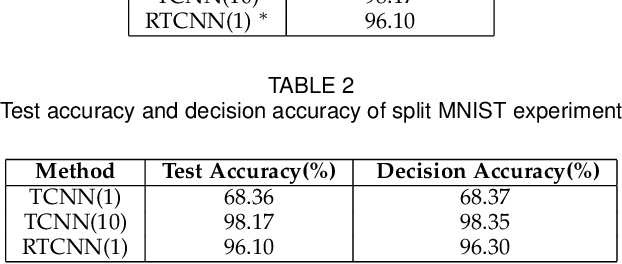
Conventional deep learning models have limited capacity in learning multiple tasks sequentially. The issue of forgetting the previously learned tasks in continual learning is known as catastrophic forgetting or interference. When the input data or the goal of learning change, a continual model will learn and adapt to the new status. However, the model will not remember or recognise any revisits to the previous states. This causes performance reduction and re-training curves in dealing with periodic or irregularly reoccurring changes in the data or goals. The changes in goals or data are referred to as new tasks in a continual learning model. Most of the continual learning methods have a task-known setup in which the task identities are known in advance to the learning model. We propose Task Conditional Neural Networks (TCNN) that does not require to known the reoccurring tasks in advance. We evaluate our model on standard datasets using MNIST and CIFAR10, and also a real-world dataset that we have collected in a remote healthcare monitoring study (i.e. TIHM dataset). The proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art solutions in continual learning and adapting to new tasks that are not defined in advance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge