Connection graph Laplacian methods can be made robust to noise
Paper and Code
May 23, 2014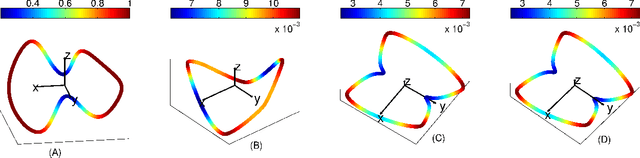
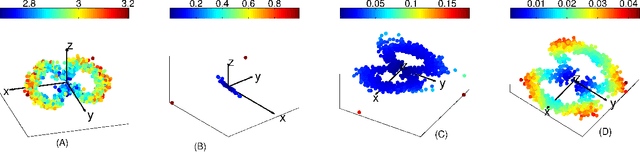
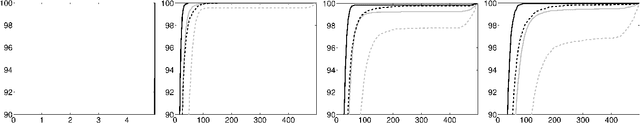
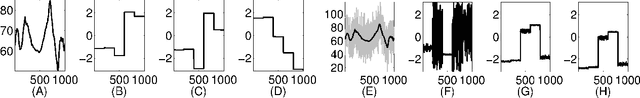
Recently, several data analytic techniques based on connection graph laplacian (CGL) ideas have appeared in the literature. At this point, the properties of these methods are starting to be understood in the setting where the data is observed without noise. We study the impact of additive noise on these methods, and show that they are remarkably robust. As a by-product of our analysis, we propose modifications of the standard algorithms that increase their robustness to noise. We illustrate our results in numerical simulations.
* 33 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge