Concept-driven Off Policy Evaluation
Paper and Code
Nov 28, 2024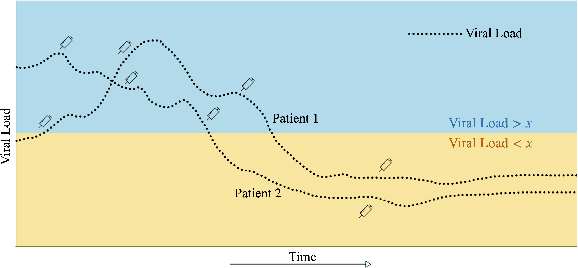
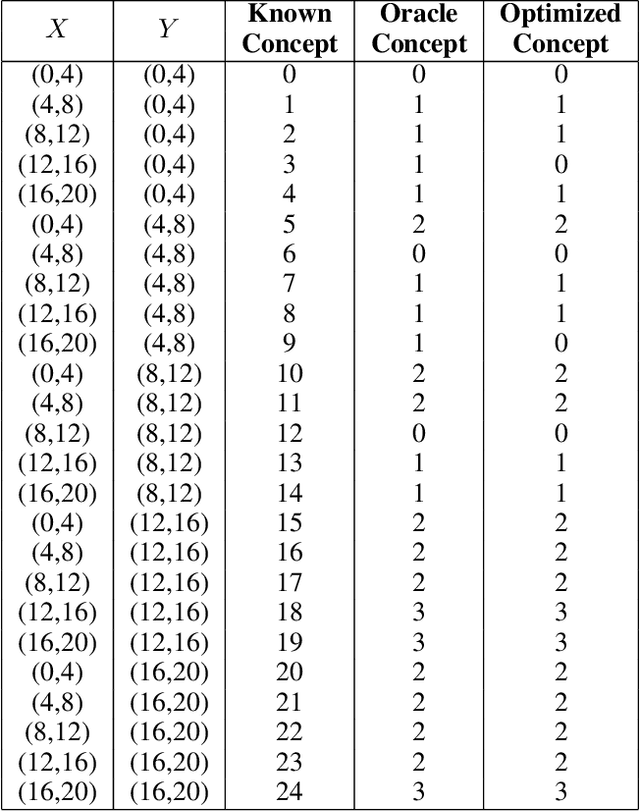
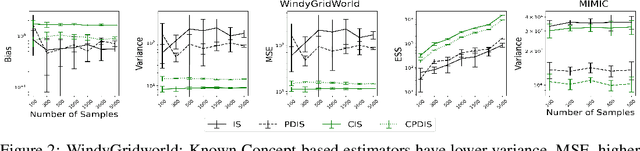
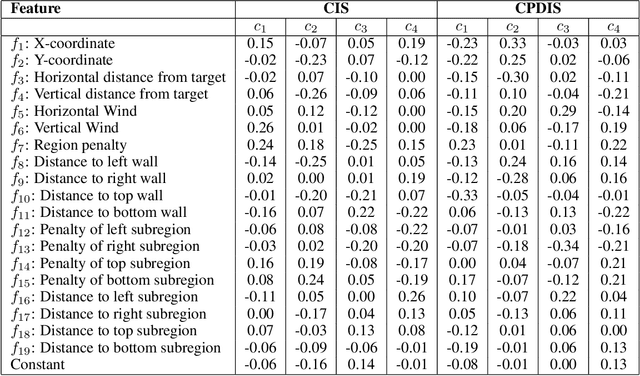
Evaluating off-policy decisions using batch data poses significant challenges due to limited sample sizes leading to high variance. To improve Off-Policy Evaluation (OPE), we must identify and address the sources of this variance. Recent research on Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) shows that using human-explainable concepts can improve predictions and provide better understanding. We propose incorporating concepts into OPE to reduce variance. Our work introduces a family of concept-based OPE estimators, proving that they remain unbiased and reduce variance when concepts are known and predefined. Since real-world applications often lack predefined concepts, we further develop an end-to-end algorithm to learn interpretable, concise, and diverse parameterized concepts optimized for variance reduction. Our experiments with synthetic and real-world datasets show that both known and learned concept-based estimators significantly improve OPE performance. Crucially, we show that, unlike other OPE methods, concept-based estimators are easily interpretable and allow for targeted interventions on specific concepts, further enhancing the quality of these estimators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge