ConAM: Confidence Attention Module for Convolutional Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Oct 27, 2021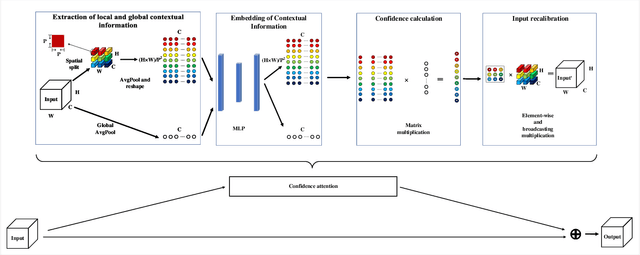
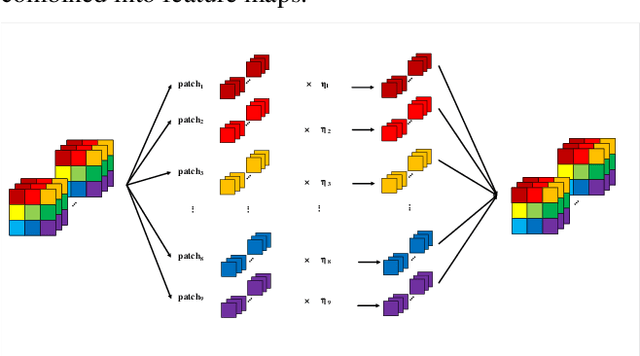

The so-called ``attention'' is an efficient mechanism to improve the performance of convolutional neural networks. It uses contextual information to recalibrate the input to strengthen the propagation of informative features. However, the majority of the attention mechanisms only consider either local or global contextual information, which is singular to extract features. Moreover, many existing mechanisms directly use the contextual information to recalibrate the input, which unilaterally enhances the propagation of the informative features, but does not suppress the useless ones. This paper proposes a new attention mechanism module based on the correlation between local and global contextual information and we name this correlation as confidence. The novel attention mechanism extracts the local and global contextual information simultaneously, and calculates the confidence between them, then uses this confidence to recalibrate the input pixels. The extraction of local and global contextual information increases the diversity of features. The recalibration with confidence suppresses useless information while enhancing the informative one with fewer parameters. We use CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 in our experiments and explore the performance of our method's components by sufficient ablation studies. Finally, we compare our method with a various state-of-the-art convolutional neural networks and the results show that our method completely surpasses these models. We implement ConAM with the Python library, Pytorch, and the code and models will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge