Computational Red Teaming in a Sudoku Solving Context: Neural Network Based Skill Representation and Acquisition
Paper and Code
Feb 27, 2018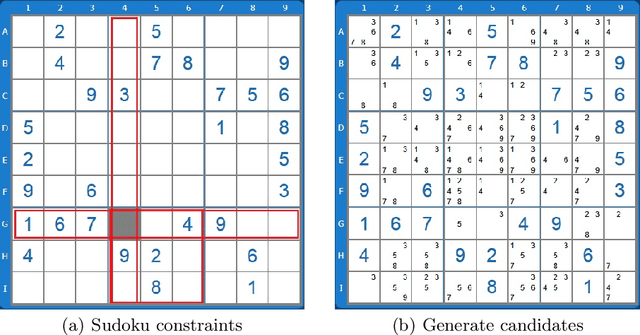

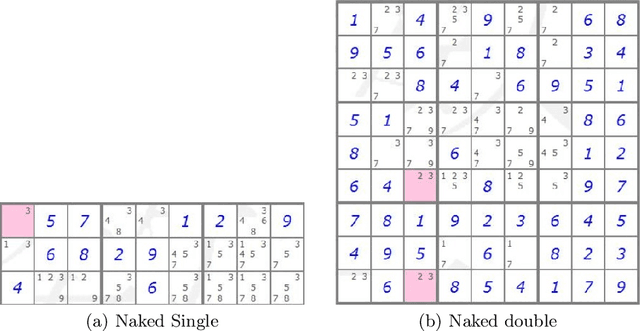
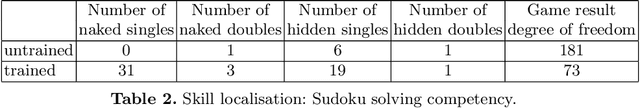
In this paper we provide an insight into the skill representation, where skill representation is seen as an essential part of the skill assessment stage in the Computational Red Teaming process. Skill representation is demonstrated in the context of Sudoku puzzle, for which the real human skills used in Sudoku solving, along with their acquisition, are represented computationally in a cognitively plausible manner, by using feed-forward neural networks with back-propagation, and supervised learning. The neural network based skills are then coupled with a hard-coded constraint propagation computational Sudoku solver, in which the solving sequence is kept hard-coded, and the skills are represented through neural networks. The paper demonstrates that the modified solver can achieve different levels of proficiency, depending on the amount of skills acquired through the neural networks. Results are encouraging for developing more complex skill and skill acquisition models usable in general frameworks related to the skill assessment aspect of Computational Red Teaming.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge