Computational Attention System for Children, Adults and Elderly
Paper and Code
Apr 18, 2019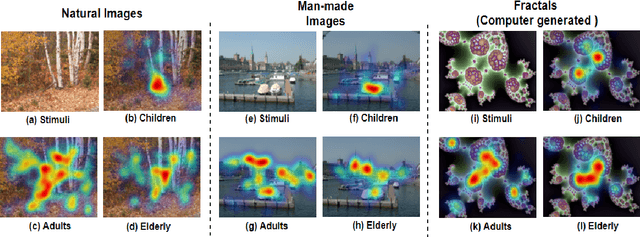
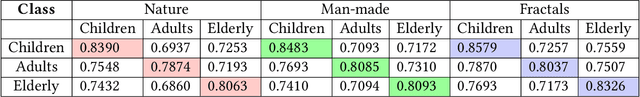

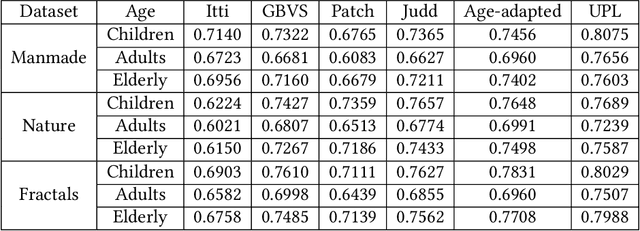
The existing computational visual attention systems have focused on the objective to basically simulate and understand the concept of visual attention system in adults. Consequently, the impact of observer's age in scene viewing behavior has rarely been considered. This study quantitatively analyzed the age-related differences in gaze landings during scene viewing for three different class of images: naturals, man-made, and fractals. Observer's of different age-group have shown different scene viewing tendencies independent to the class of the image viewed. Several interesting observations are drawn from the results. First, gaze landings for man-made dataset showed that whereas child observers focus more on the scene foreground, i.e., locations that are near, elderly observers tend to explore the scene background, i.e., locations farther in the scene. Considering this result a framework is proposed in this paper to quantitatively measure the depth bias tendency across age groups. Second, the quantitative analysis results showed that children exhibit the lowest exploratory behavior level but the highest central bias tendency among the age groups and across the different scene categories. Third, inter-individual similarity metrics reveal that an adult had significantly lower gaze consistency with children and elderly compared to other adults for all the scene categories. Finally, these analysis results were consequently leveraged to develop a more accurate age-adapted saliency model independent to the image type. The prediction accuracy suggests that our model fits better to the collected eye-gaze data of the observers belonging to different age groups than the existing models do.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge