Complementing Handcrafted Features with Raw Waveform Using a Light-weight Auxiliary Model
Paper and Code
Sep 06, 2021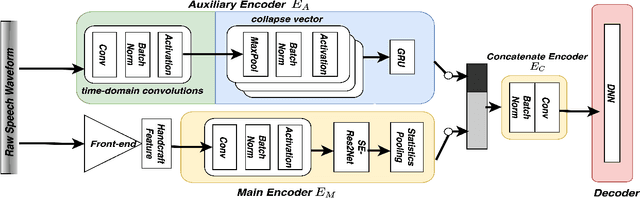
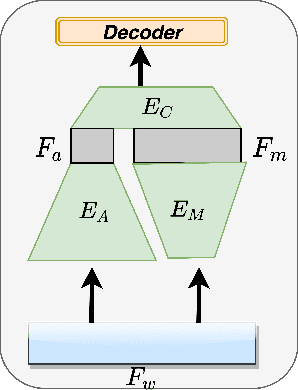
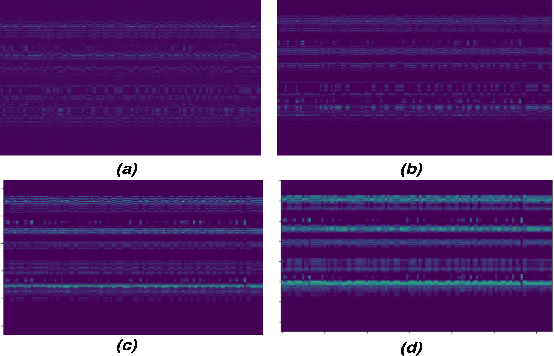
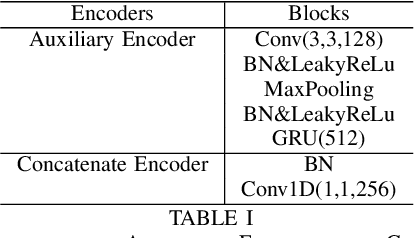
An emerging trend in audio processing is capturing low-level speech representations from raw waveforms. These representations have shown promising results on a variety of tasks, such as speech recognition and speech separation. Compared to handcrafted features, learning speech features via backpropagation provides the model greater flexibility in how it represents data for different tasks theoretically. However, results from empirical study shows that, in some tasks, such as voice spoof detection, handcrafted features are more competitive than learned features. Instead of evaluating handcrafted features and raw waveforms independently, this paper proposes an Auxiliary Rawnet model to complement handcrafted features with features learned from raw waveforms. A key benefit of the approach is that it can improve accuracy at a relatively low computational cost. The proposed Auxiliary Rawnet model is tested using the ASVspoof 2019 dataset and the results from this dataset indicate that a light-weight waveform encoder can potentially boost the performance of handcrafted-features-based encoders in exchange for a small amount of additional computational work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge