Comparison of Short Blocklength Slepian-Wolf Coding for Key Reconciliation
Paper and Code
Mar 21, 2021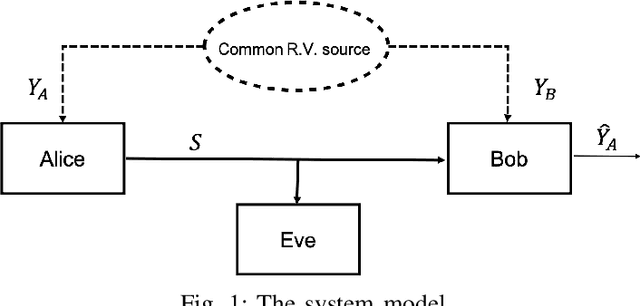
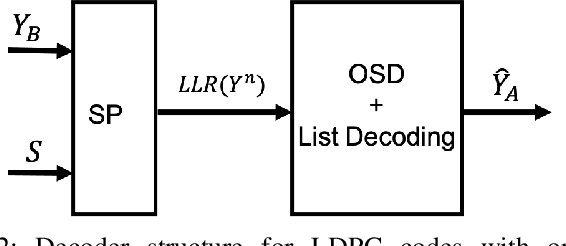
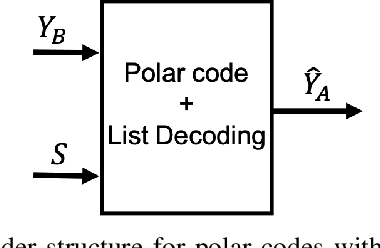
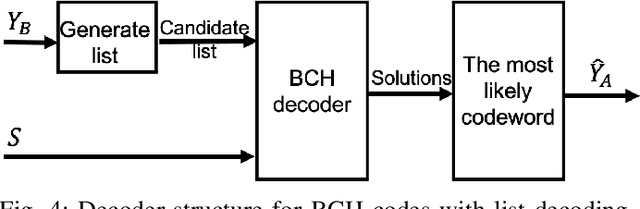
We focus Slepian-Wolf (SW) coding in the short blocklength for reconciliation in secret key generation and physical unclonable functions. In the problem formulation, two legitimate parties wish to generate a common secret key from a noisy observation of a common random source in the presence of a passive eavesdropper. We consider three different families of codes for key reconciliation. The selected codes show promising performances in information transmission in the short block-length regime. We implement and compare the performance of different codes for SW reconciliation in the terms of reliability and decoding complexity.
* arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2010.14457
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge