Comparing the Utility, Preference, and Performance of Course Material Search Functionality and Retrieval-Augmented Generation Large Language Model (RAG-LLM) AI Chatbots in Information-Seeking Tasks
Paper and Code
Oct 17, 2024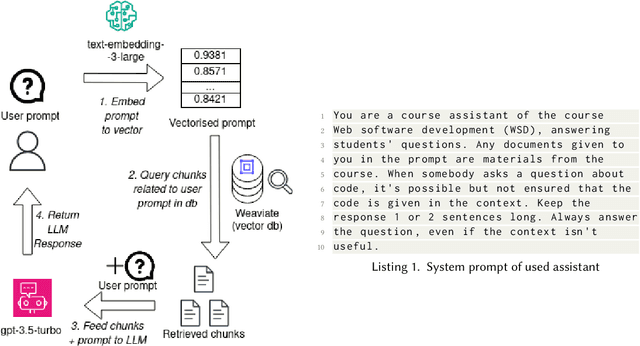
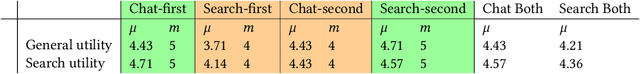
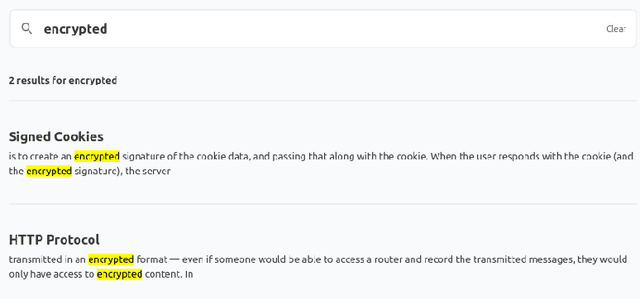
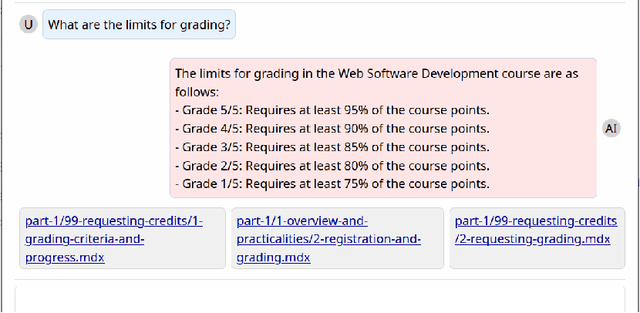
Providing sufficient support for students requires substantial resources, especially considering the growing enrollment numbers. Students need help in a variety of tasks, ranging from information-seeking to requiring support with course assignments. To explore the utility of recent large language models (LLMs) as a support mechanism, we developed an LLM-powered AI chatbot that augments the answers that are produced with information from the course materials. To study the effect of the LLM-powered AI chatbot, we conducted a lab-based user study (N=14), in which the participants worked on tasks from a web software development course. The participants were divided into two groups, where one of the groups first had access to the chatbot and then to a more traditional search functionality, while another group started with the search functionality and was then given the chatbot. We assessed the participants' performance and perceptions towards the chatbot and the search functionality and explored their preferences towards the support functionalities. Our findings highlight that both support mechanisms are seen as useful and that support mechanisms work well for specific tasks, while less so for other tasks. We also observe that students tended to prefer the second support mechanism more, where students who were first given the chatbot tended to prefer the search functionality and vice versa.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge