Collaborative Remote Control of Unmanned Ground Vehicles in Virtual Reality
Paper and Code
Aug 24, 2022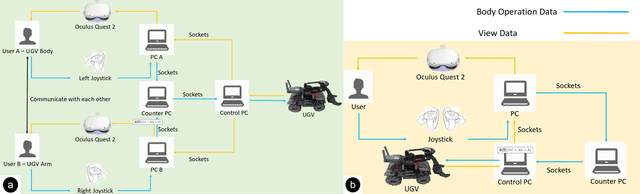
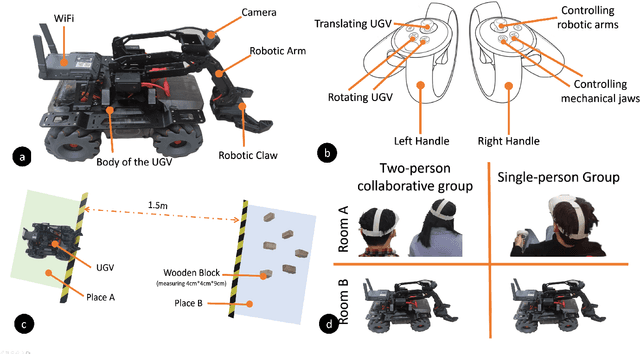
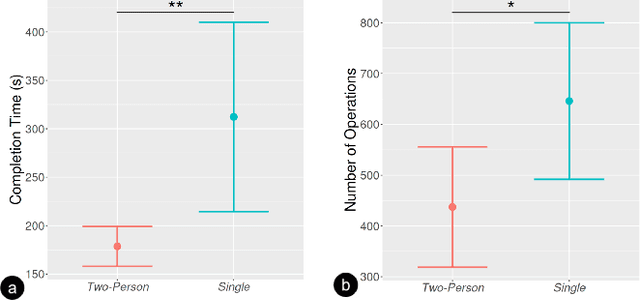
Virtual reality (VR) technology is commonly used in entertainment applications; however, it has also been deployed in practical applications in more serious aspects of our lives, such as safety. To support people working in dangerous industries, VR can ensure operators manipulate standardized tasks and work collaboratively to deal with potential risks. Surprisingly, little research has focused on how people can collaboratively work in VR environments. Few studies have paid attention to the cognitive load of operators in their collaborative tasks. Once task demands become complex, many researchers focus on optimizing the design of the interaction interfaces to reduce the cognitive load on the operator. That approach could be of merit; however, it can actually subject operators to a more significant cognitive load and potentially more errors and a failure of collaboration. In this paper, we propose a new collaborative VR system to support two teleoperators working in the VR environment to remote control an uncrewed ground vehicle. We use a compared experiment to evaluate the collaborative VR systems, focusing on the time spent on tasks and the total number of operations. Our results show that the total number of processes and the cognitive load during operations were significantly lower in the two-person group than in the single-person group. Our study sheds light on designing VR systems to support collaborative work with respect to the flow of work of teleoperators instead of simply optimizing the design outcomes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge