Collaborative Intelligence in Sequential Experiments: A Human-in-the-Loop Framework for Drug Discovery
Paper and Code
May 07, 2024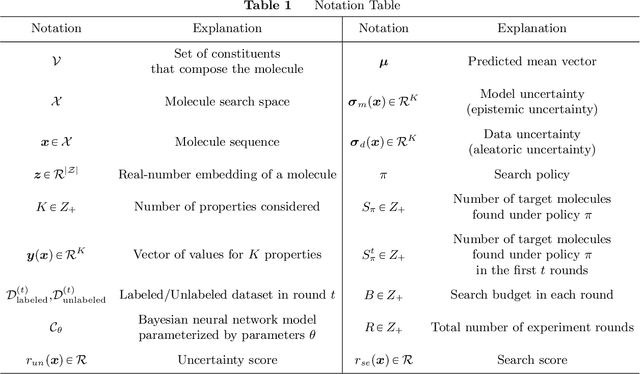
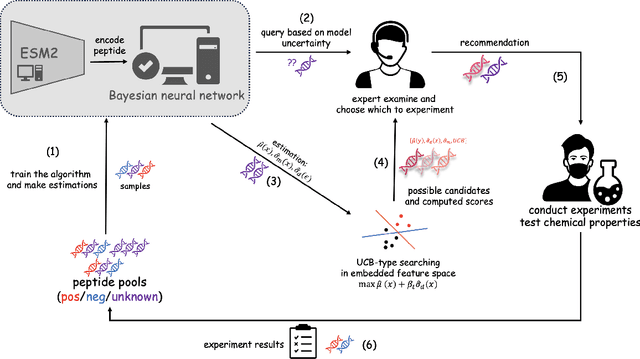
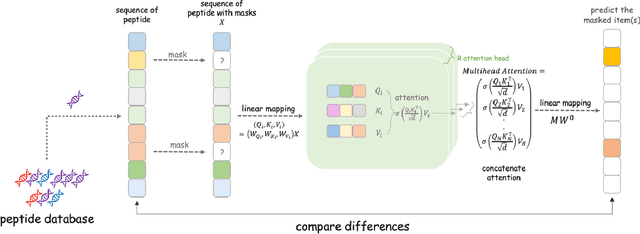
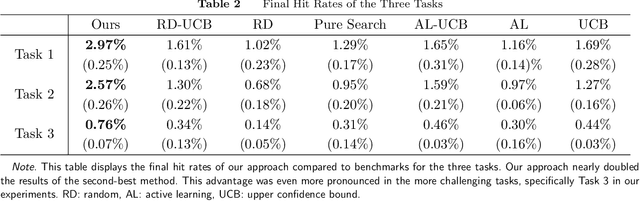
Drug discovery is a complex process that involves sequentially screening and examining a vast array of molecules to identify those with the target properties. This process, also referred to as sequential experimentation, faces challenges due to the vast search space, the rarity of target molecules, and constraints imposed by limited data and experimental budgets. To address these challenges, we introduce a human-in-the-loop framework for sequential experiments in drug discovery. This collaborative approach combines human expert knowledge with deep learning algorithms, enhancing the discovery of target molecules within a specified experimental budget. The proposed algorithm processes experimental data to recommend both promising molecules and those that could improve its performance to human experts. Human experts retain the final decision-making authority based on these recommendations and their domain expertise, including the ability to override algorithmic recommendations. We applied our method to drug discovery tasks using real-world data and found that it consistently outperforms all baseline methods, including those which rely solely on human or algorithmic input. This demonstrates the complementarity between human experts and the algorithm. Our results provide key insights into the levels of humans' domain knowledge, the importance of meta-knowledge, and effective work delegation strategies. Our findings suggest that such a framework can significantly accelerate the development of new vaccines and drugs by leveraging the best of both human and artificial intelligence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge