Coarse-to-Fine Memory Matching for Joint Retrieval and Classification
Paper and Code
Nov 29, 2020
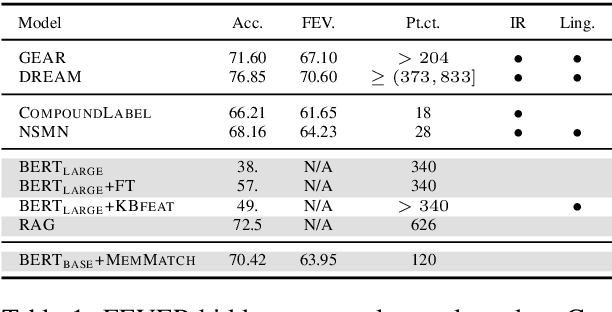
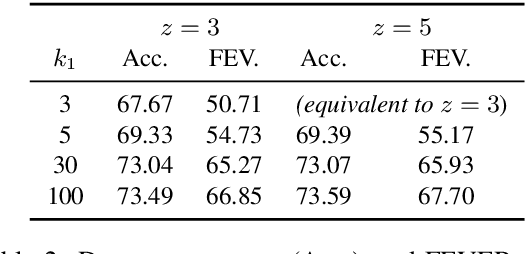
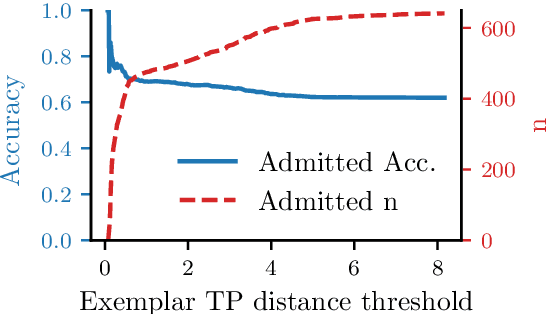
We present a novel end-to-end language model for joint retrieval and classification, unifying the strengths of bi- and cross- encoders into a single language model via a coarse-to-fine memory matching search procedure for learning and inference. Evaluated on the standard blind test set of the FEVER fact verification dataset, classification accuracy is significantly higher than approaches that only rely on the language model parameters as a knowledge base, and approaches some recent multi-model pipeline systems, using only a single BERT base model augmented with memory layers. We further demonstrate how coupled retrieval and classification can be leveraged to identify low confidence instances, and we extend exemplar auditing to this setting for analyzing and constraining the model. As a result, our approach yields a means of updating language model behavior through two distinct mechanisms: The retrieved information can be updated explicitly, and the model behavior can be modified via the exemplar database.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge