Clustering with Missing Features: A Penalized Dissimilarity Measure based approach
Paper and Code
Jul 07, 2018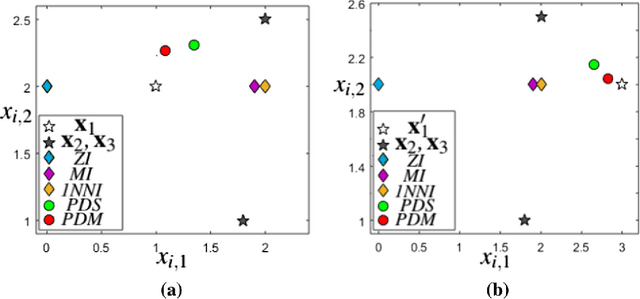

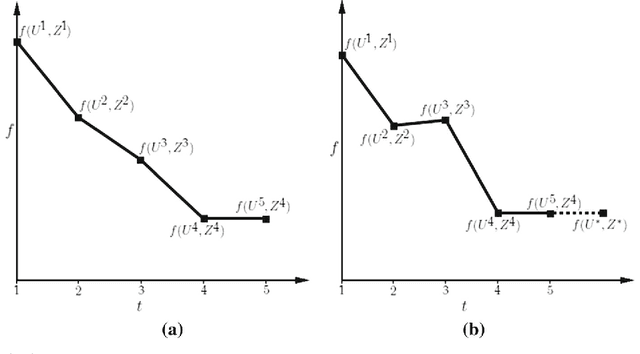
Many real-world clustering problems are plagued by incomplete data characterized by missing or absent features for some or all of the data instances. Traditional clustering methods cannot be directly applied to such data without preprocessing by imputation or marginalization techniques. In this article, we overcome this drawback by utilizing a penalized dissimilarity measure which we refer to as the Feature Weighted Penalty based Dissimilarity (FWPD). Using the FWPD measure, we modify the traditional k-means clustering algorithm and the standard hierarchical agglomerative clustering algorithms so as to make them directly applicable to datasets with missing features. We present time complexity analyses for these new techniques and also undertake a detailed theoretical analysis showing that the new FWPD based k-means algorithm converges to a local optimum within a finite number of iterations. We also present a detailed method for simulating random as well as feature dependent missingness. We report extensive experiments on various benchmark datasets for different types of missingness showing that the proposed clustering techniques have generally better results compared to some of the most well-known imputation methods which are commonly used to handle such incomplete data. We append a possible extension of the proposed dissimilarity measure to the case of absent features (where the unobserved features are known to be undefined).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge