Clustering with feature selection using alternating minimization, Application to computational biology
Paper and Code
Oct 29, 2018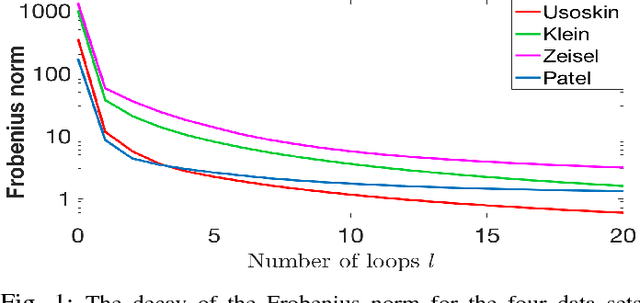
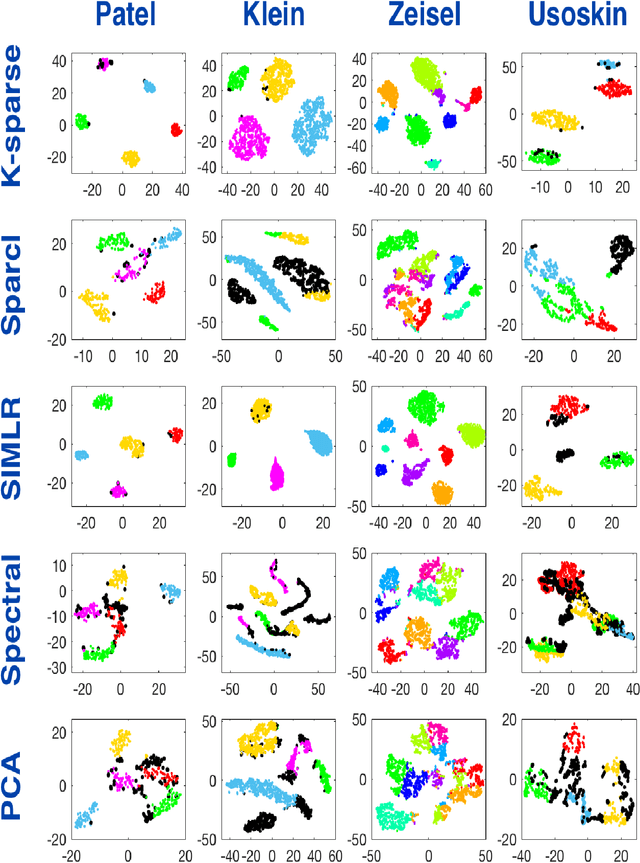
This paper deals with unsupervised clustering with feature selection. The problem is to estimate both labels and a sparse projection matrix of weights. To address this combinatorial non-convex problem maintaining a strict control on the sparsity of the matrix of weights, we propose an alternating minimization of the Frobenius norm criterion. We provide a new efficient algorithm named K-sparse which alternates k-means with projection-gradient minimization. The projection-gradient step is a method of splitting type, with exact projection on the $\ell^1$ ball to promote sparsity. The convergence of the gradient-projection step is addressed, and a preliminary analysis of the alternating minimization is made. The Frobenius norm criterion converges as the number of iterates in Algorithm K-sparse goes to infinity. Experiments on Single Cell RNA sequencing datasets show that our method significantly improves the results of PCA k-means, spectral clustering, SIMLR, and Sparcl methods, and achieves a relevant selection of genes. The complexity of K-sparse is linear in the number of samples (cells), so that the method scales up to large datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge