Clustering by Deep Nearest Neighbor Descent : A Density-based Parameter-Insensitive Clustering Method
Paper and Code
Dec 07, 2015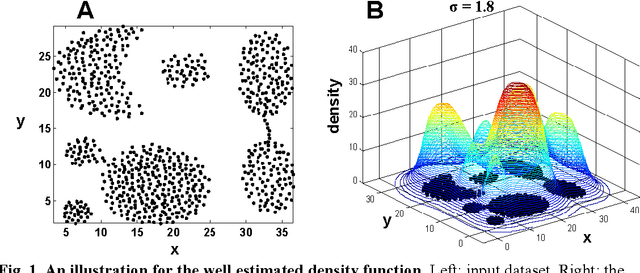
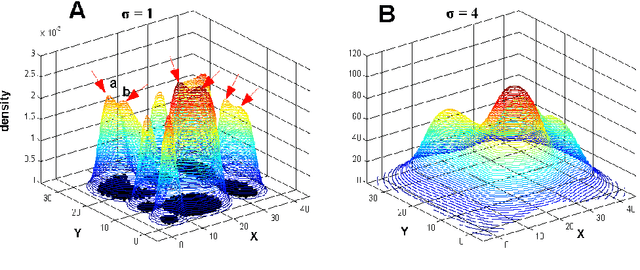
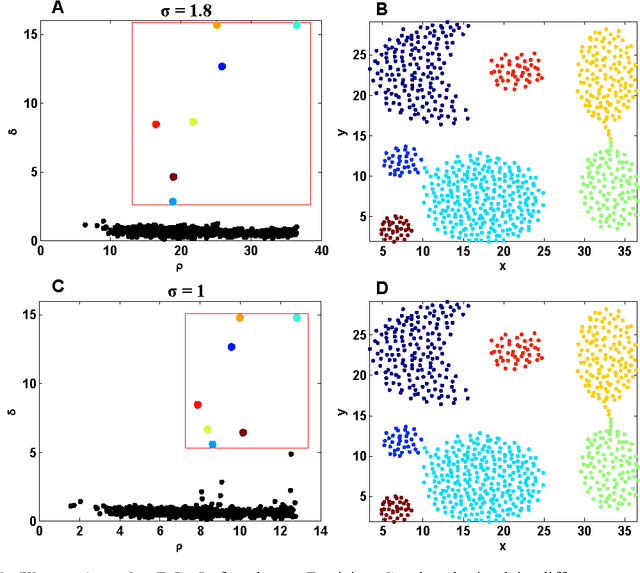
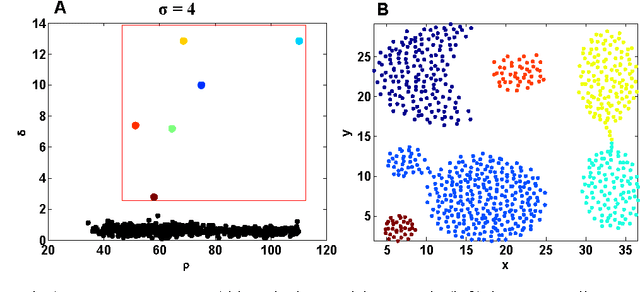
Most density-based clustering methods largely rely on how well the underlying density is estimated. However, density estimation itself is also a challenging problem, especially the determination of the kernel bandwidth. A large bandwidth could lead to the over-smoothed density estimation in which the number of density peaks could be less than the true clusters, while a small bandwidth could lead to the under-smoothed density estimation in which spurious density peaks, or called the "ripple noise", would be generated in the estimated density. In this paper, we propose a density-based hierarchical clustering method, called the Deep Nearest Neighbor Descent (D-NND), which could learn the underlying density structure layer by layer and capture the cluster structure at the same time. The over-smoothed density estimation could be largely avoided and the negative effect of the under-estimated cases could be also largely reduced. Overall, D-NND presents not only the strong capability of discovering the underlying cluster structure but also the remarkable reliability due to its insensitivity to parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge