City-scale Pollution Aware Traffic Routing by Sampling Max Flows using MCMC
Paper and Code
Feb 28, 2023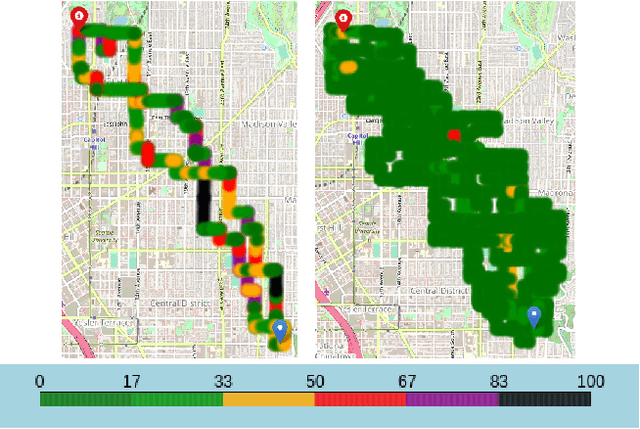
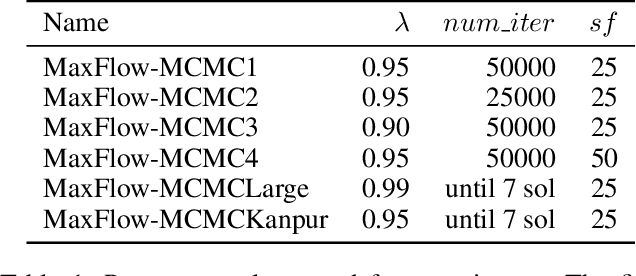
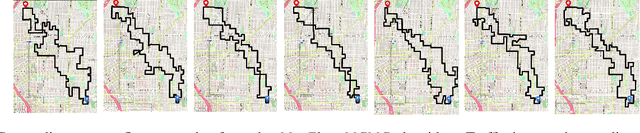
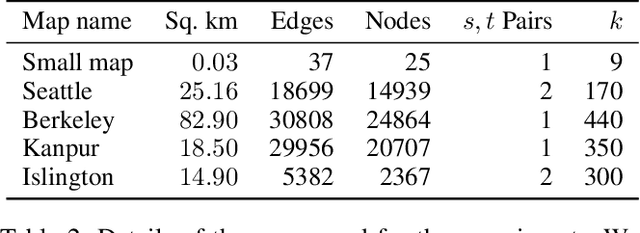
A significant cause of air pollution in urban areas worldwide is the high volume of road traffic. Long-term exposure to severe pollution can cause serious health issues. One approach towards tackling this problem is to design a pollution-aware traffic routing policy that balances multiple objectives of i) avoiding extreme pollution in any area ii) enabling short transit times, and iii) making effective use of the road capacities. We propose a novel sampling-based approach for this problem. We provide the first construction of a Markov Chain that can sample integer max flow solutions of a planar graph, with theoretical guarantees that the probabilities depend on the aggregate transit length. We designed a traffic policy using diverse samples and simulated traffic on real-world road maps using the SUMO traffic simulator. We observe a considerable decrease in areas with severe pollution when experimented with maps of large cities across the world compared to other approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge