Characterizing Error in Noncommutative Geometric Gait Analysis
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2022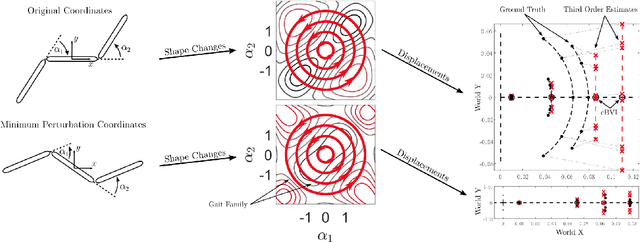
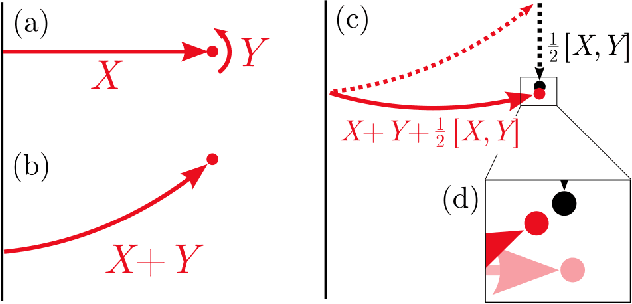
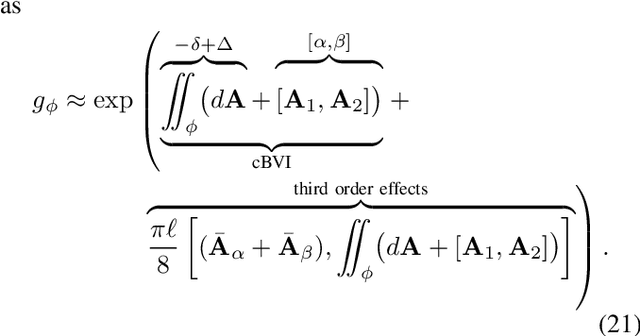
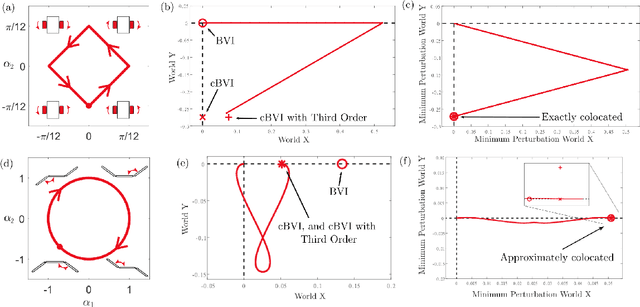
A key problem in robotic locomotion is in finding optimal shape changes to effectively displace systems through the world. Variational techniques for gait optimization require estimates of body displacement per gait cycle; however, these estimates introduce error due to unincluded high order terms. In this paper, we formulate existing estimates for displacement, and describe the contribution of low order terms to these estimates. We additionally describe the magnitude of higher (third) order effects, and identify that choice of body coordinate, gait diameter, and starting phase influence these effects. We demonstrate that variation of such parameters on two example systems (the differential drive car and Purcell swimmer) effectively manages third order contributions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge