Channel Estimation for BIOS-Assisted Multi-User MIMO Systems: A Heterogeneous Two-timescale Strategy
Paper and Code
Feb 16, 2023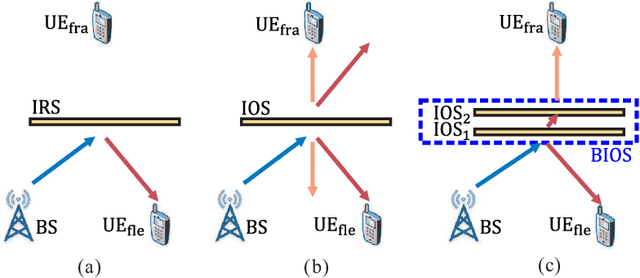
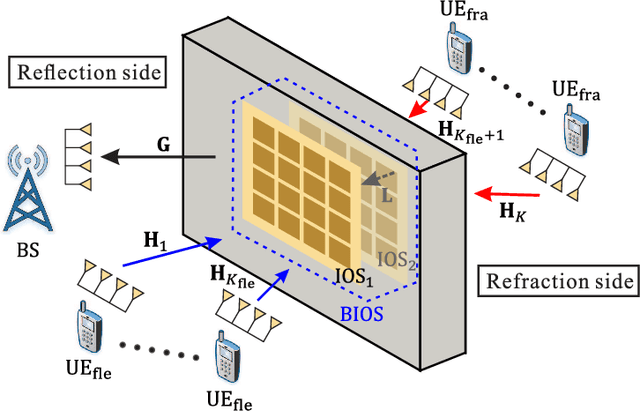
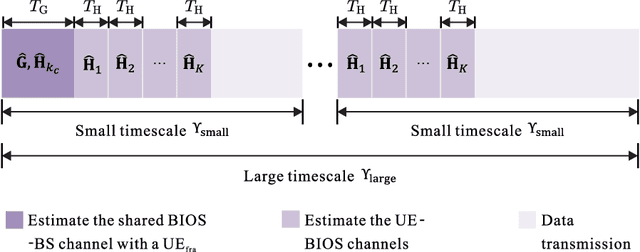

Bilayer intelligent omni-surface (BIOS) has recently attracted increasing attention due to its capability of independent beamforming on both reflection and refraction sides. However, its specific bilayer structure makes the channel estimation problem more challenging than the conventional intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) or intelligent omni-surface (IOS). In this paper, we investigate the channel estimation problem in the BIOS-assisted multi-user multiple-input multiple-output system. We find that in contrast to the IRS or IOS, where the forms of the cascaded channels of all user equipments (UEs) are the same, in the BIOS, those of the UEs on the reflection side are different from those on the refraction side, which is referred to as the heterogeneous channel property. By exploiting it along with the two-timescale and sparsity properties of channels and applying the manifold optimization method, we propose an efficient channel estimation scheme to reduce the training overhead in the BIOS-assisted system. Moreover, we investigate the joint optimization of base station digital beamforming and BIOS passive analog beamforming. Simulation results show that the proposed estimation scheme can significantly reduce the training overhead with competitive estimation quality, and thus keeps the performance advantage of BIOS over IRS and IOS with imperfect channel state information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge