Can We Break Free from Strong Data Augmentations in Self-Supervised Learning?
Paper and Code
Apr 15, 2024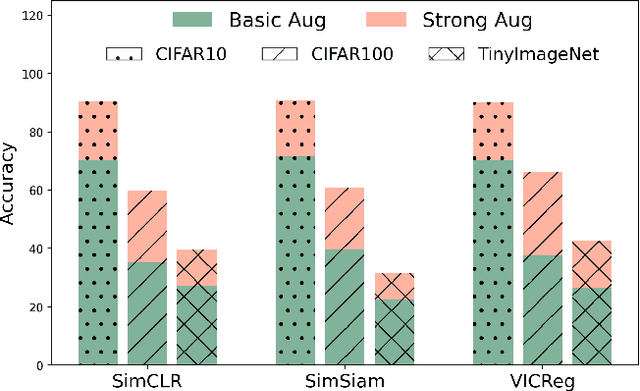

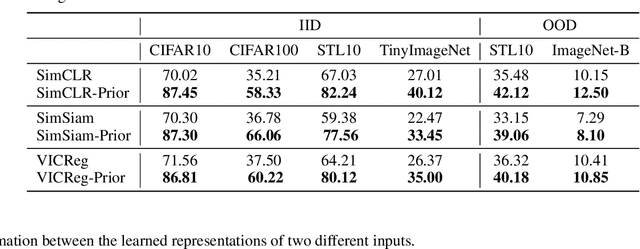
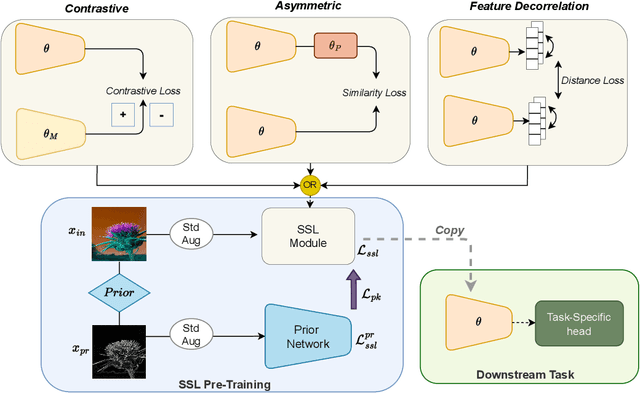
Self-supervised learning (SSL) has emerged as a promising solution for addressing the challenge of limited labeled data in deep neural networks (DNNs), offering scalability potential. However, the impact of design dependencies within the SSL framework remains insufficiently investigated. In this study, we comprehensively explore SSL behavior across a spectrum of augmentations, revealing their crucial role in shaping SSL model performance and learning mechanisms. Leveraging these insights, we propose a novel learning approach that integrates prior knowledge, with the aim of curtailing the need for extensive data augmentations and thereby amplifying the efficacy of learned representations. Notably, our findings underscore that SSL models imbued with prior knowledge exhibit reduced texture bias, diminished reliance on shortcuts and augmentations, and improved robustness against both natural and adversarial corruptions. These findings not only illuminate a new direction in SSL research, but also pave the way for enhancing DNN performance while concurrently alleviating the imperative for intensive data augmentation, thereby enhancing scalability and real-world problem-solving capabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge