Can We Assess Mental Health through Social Media and Smart Devices? Addressing Bias in Methodology and Evaluation
Paper and Code
Jul 19, 2018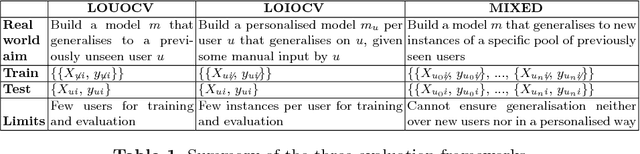
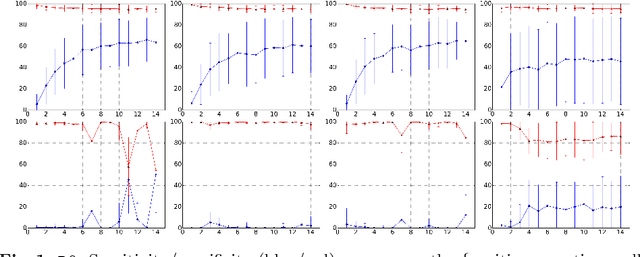
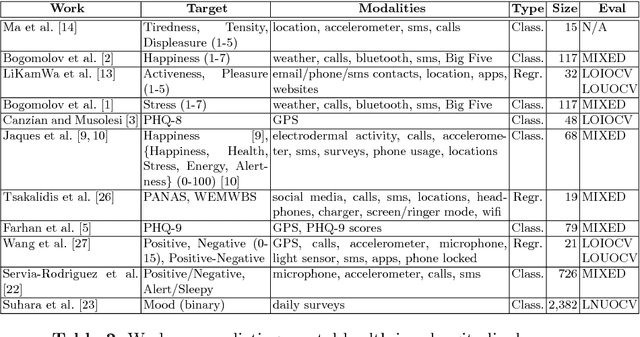
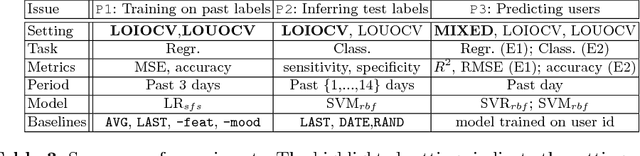
Predicting mental health from smartphone and social media data on a longitudinal basis has recently attracted great interest, with very promising results being reported across many studies. Such approaches have the potential to revolutionise mental health assessment, if their development and evaluation follows a real world deployment setting. In this work we take a closer look at state-of-the-art approaches, using different mental health datasets and indicators, different feature sources and multiple simulations, in order to assess their ability to generalise. We demonstrate that under a pragmatic evaluation framework, none of the approaches deliver or even approach the reported performances. In fact, we show that current state-of-the-art approaches can barely outperform the most na\"ive baselines in the real-world setting, posing serious questions not only about their deployment ability, but also about the contribution of the derived features for the mental health assessment task and how to make better use of such data in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge