Can Models Learn Skill Composition from Examples?
Paper and Code
Sep 29, 2024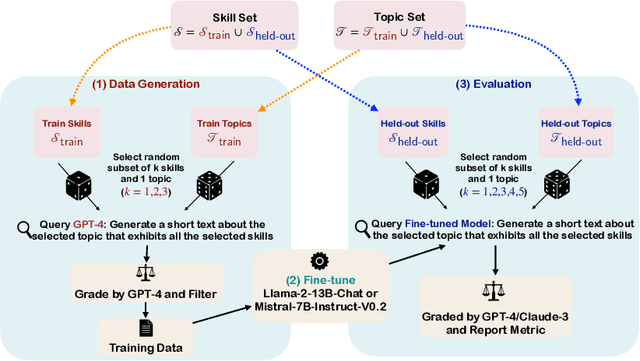

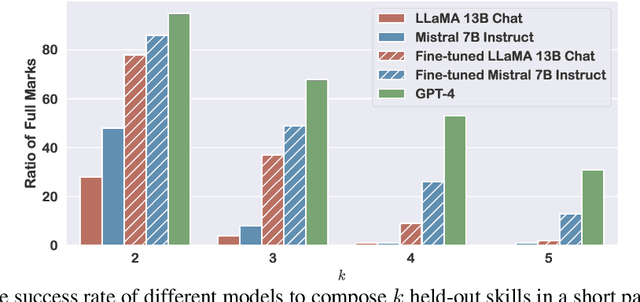

As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly advanced, their ability to exhibit compositional generalization -- the capacity to combine learned skills in novel ways not encountered during training -- has garnered significant attention. This type of generalization, particularly in scenarios beyond training data, is also of great interest in the study of AI safety and alignment. A recent study introduced the SKILL-MIX evaluation, where models are tasked with composing a short paragraph demonstrating the use of a specified $k$-tuple of language skills. While small models struggled with composing even with $k=3$, larger models like GPT-4 performed reasonably well with $k=5$ and $6$. In this paper, we employ a setup akin to SKILL-MIX to evaluate the capacity of smaller models to learn compositional generalization from examples. Utilizing a diverse set of language skills -- including rhetorical, literary, reasoning, theory of mind, and common sense -- GPT-4 was used to generate text samples that exhibit random subsets of $k$ skills. Subsequent fine-tuning of 7B and 13B parameter models on these combined skill texts, for increasing values of $k$, revealed the following findings: (1) Training on combinations of $k=2$ and $3$ skills results in noticeable improvements in the ability to compose texts with $k=4$ and $5$ skills, despite models never having seen such examples during training. (2) When skill categories are split into training and held-out groups, models significantly improve at composing texts with held-out skills during testing despite having only seen training skills during fine-tuning, illustrating the efficacy of the training approach even with previously unseen skills. This study also suggests that incorporating skill-rich (potentially synthetic) text into training can substantially enhance the compositional capabilities of models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge