Can Language Representation Models Think in Bets?
Paper and Code
Oct 14, 2022
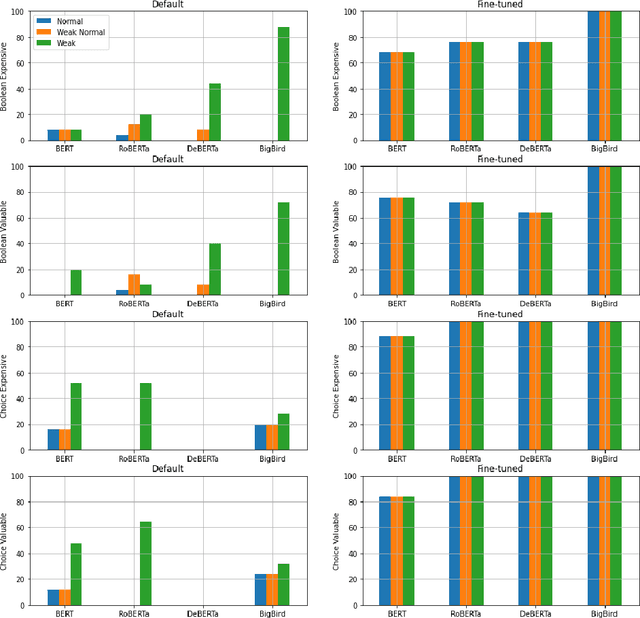
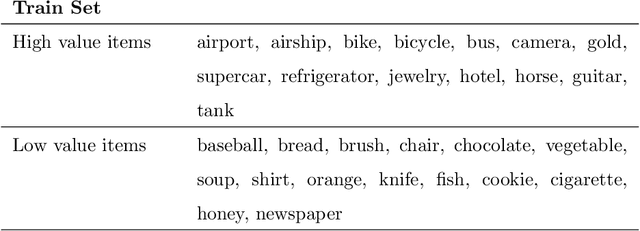
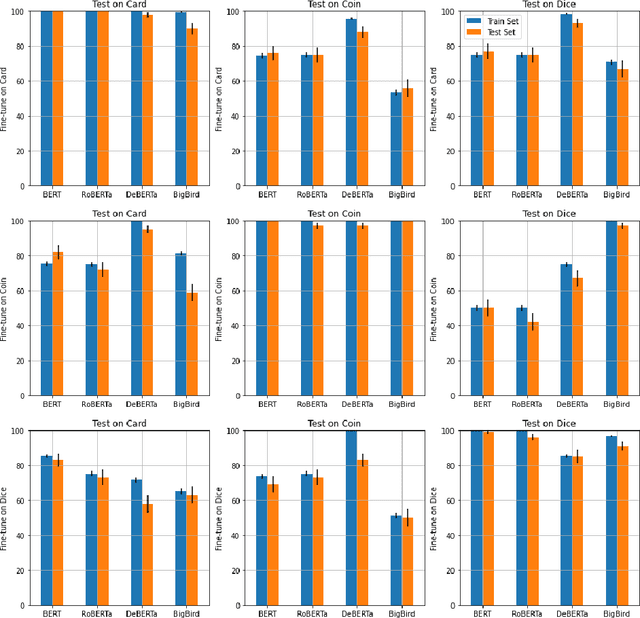
In recent years, transformer-based language representation models (LRMs) have achieved state-of-the-art results on difficult natural language understanding problems, such as question answering and text summarization. As these models are integrated into real-world applications, evaluating their ability to make rational decisions is an important research agenda, with practical ramifications. This article investigates LRMs' rational decision-making ability through a carefully designed set of decision-making benchmarks and experiments. Inspired by classic work in cognitive science, we model the decision-making problem as a bet. We then investigate an LRM's ability to choose outcomes that have optimal, or at minimum, positive expected gain. Through a robust body of experiments on four established LRMs, we show that a model is only able to `think in bets' if it is first fine-tuned on bet questions with an identical structure. Modifying the bet question's structure, while still retaining its fundamental characteristics, decreases an LRM's performance by more than 25\%, on average, although absolute performance remains well above random. LRMs are also found to be more rational when selecting outcomes with non-negative expected gain, rather than optimal or strictly positive expected gain. Our results suggest that LRMs could potentially be applied to tasks that rely on cognitive decision-making skills, but that more research is necessary before they can robustly make rational decisions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge