Calibration of Machine Reading Systems at Scale
Paper and Code
Mar 20, 2022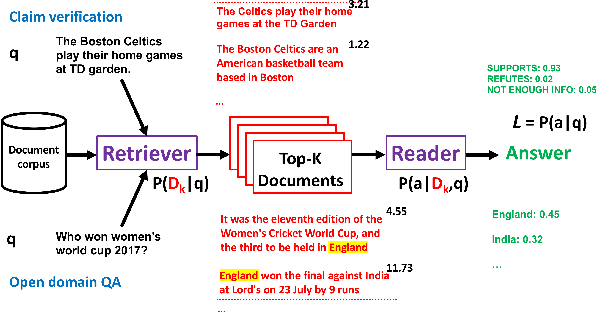
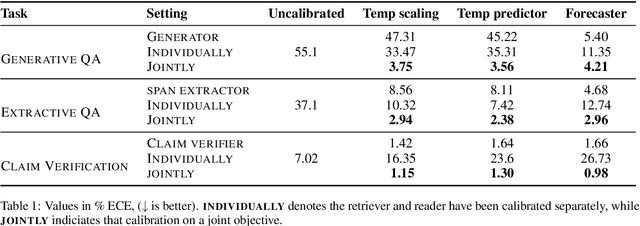

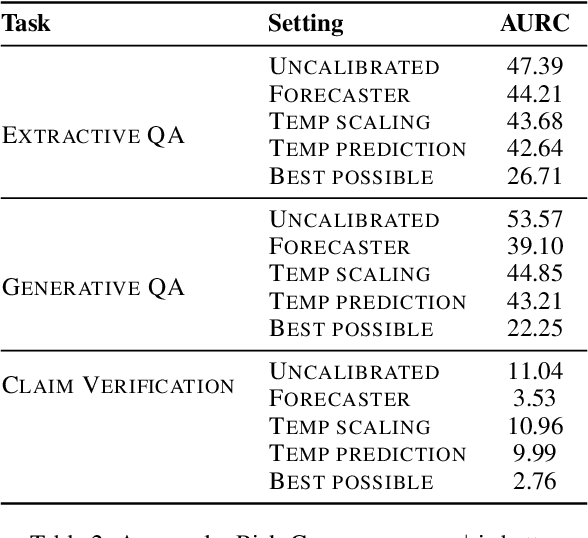
In typical machine learning systems, an estimate of the probability of the prediction is used to assess the system's confidence in the prediction. This confidence measure is usually uncalibrated; i.e.\ the system's confidence in the prediction does not match the true probability of the predicted output. In this paper, we present an investigation into calibrating open setting machine reading systems such as open-domain question answering and claim verification systems. We show that calibrating such complex systems which contain discrete retrieval and deep reading components is challenging and current calibration techniques fail to scale to these settings. We propose simple extensions to existing calibration approaches that allows us to adapt them to these settings. Our experimental results reveal that the approach works well, and can be useful to selectively predict answers when question answering systems are posed with unanswerable or out-of-the-training distribution questions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge