Bridging the gap between QP-based and MPC-based RL
Paper and Code
May 18, 2022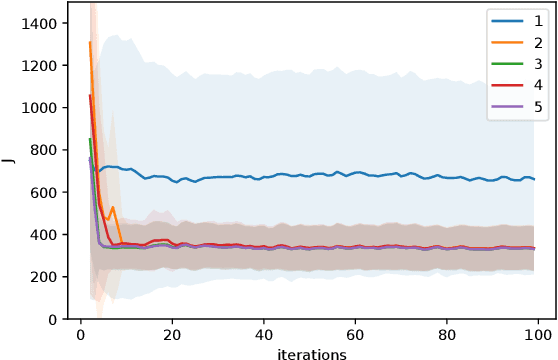
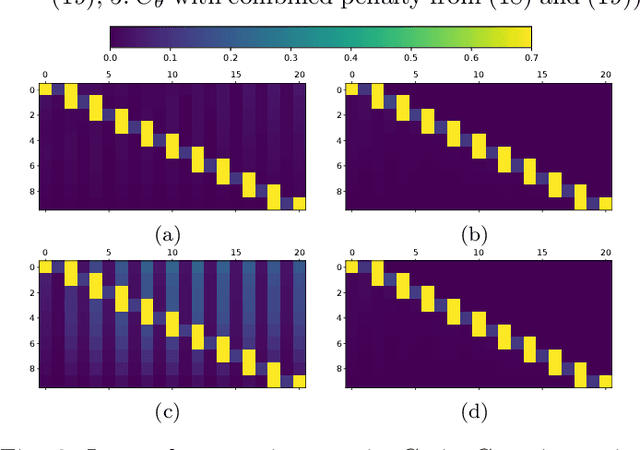
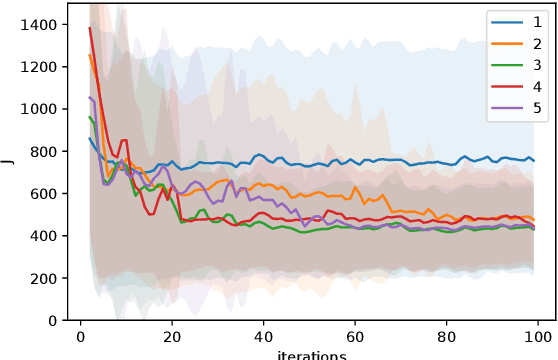
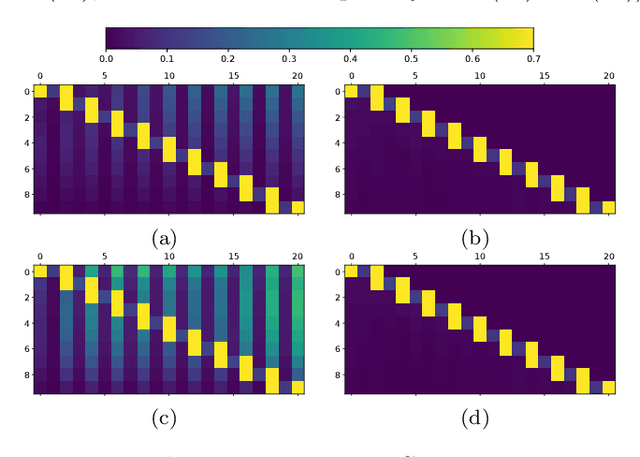
Reinforcement learning methods typically use Deep Neural Networks to approximate the value functions and policies underlying a Markov Decision Process. Unfortunately, DNN-based RL suffers from a lack of explainability of the resulting policy. In this paper, we instead approximate the policy and value functions using an optimization problem, taking the form of Quadratic Programs (QPs). We propose simple tools to promote structures in the QP, pushing it to resemble a linear MPC scheme. A generic unstructured QP offers high flexibility for learning, while a QP having the structure of an MPC scheme promotes the explainability of the resulting policy, additionally provides ways for its analysis. The tools we propose allow for continuously adjusting the trade-off between the former and the latter during learning. We illustrate the workings of our proposed method with the resulting structure using a point-mass task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge