Brain Tumor Synthetic Segmentation in 3D Multimodal MRI Scans
Paper and Code
Sep 27, 2019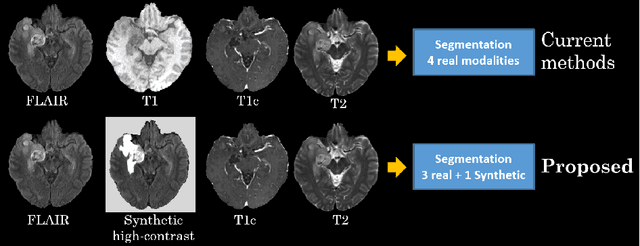
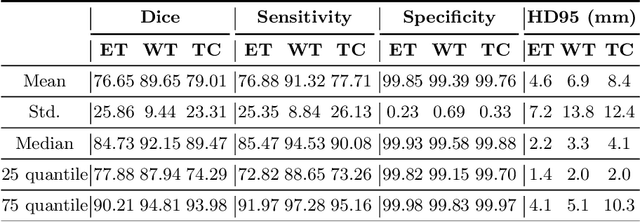
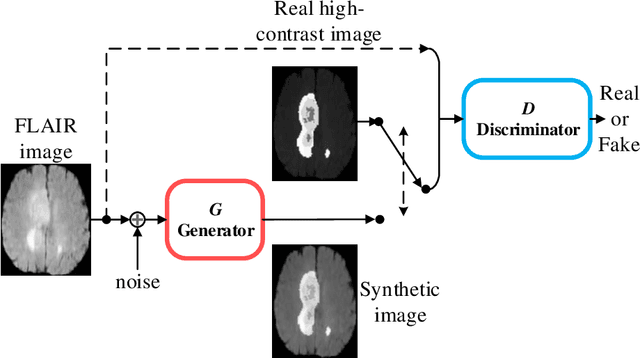
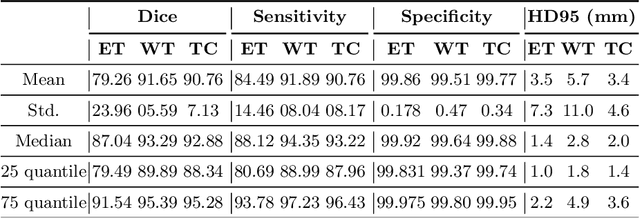
The magnetic resonance (MR) analysis of brain tumors is widely used for diagnosis and examination of tumor subregions. The overlapping area among the intensity distribution of healthy, enhancing, non-enhancing, and edema region makes the automatic segmentation a challenging task. Here, we show that a convolutional neural network trained on high-contrast images can transform intensity distribution of brain lesion in its internal subregions. Specifically, generative adversarial network (GAN) is extended to synthesize high-contrast images. A comparison of these synthetic images and real images of brain tumor tissue in MR scans showed significant segmentation improvement and decreased the number of real channels for segmentation. The synthetic images are used as a substitute for real channels and can bypass real modalities in the multimodal brain tumor segmentation framework. Segmentation results on BraTS 2019 dataset demonstrate that our proposed approach can efficiently segment the tumor areas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge