Boosting multi-demographic federated learning for chest x-ray analysis using general-purpose self-supervised representations
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2025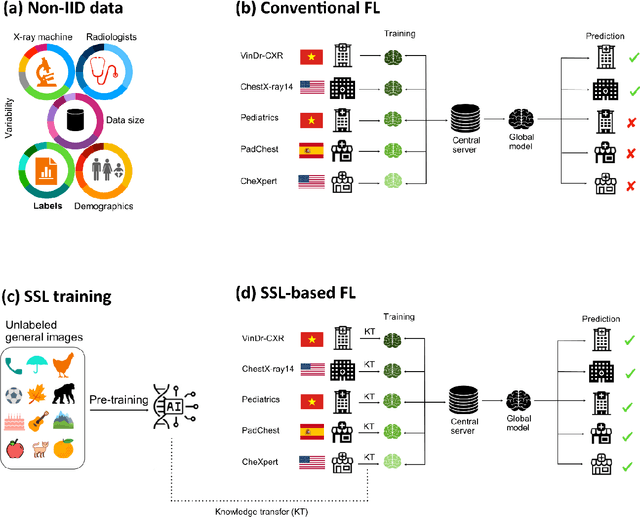
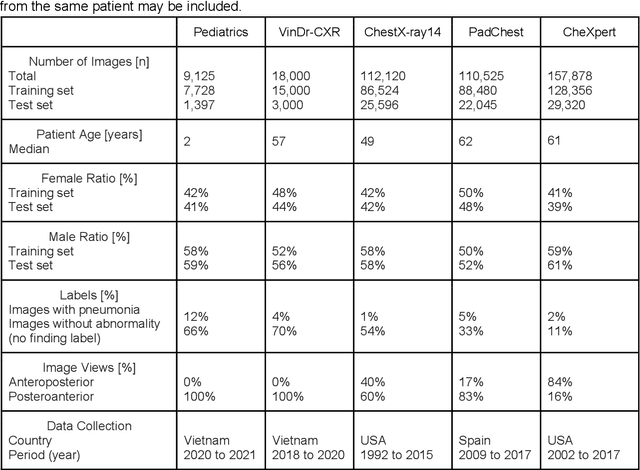
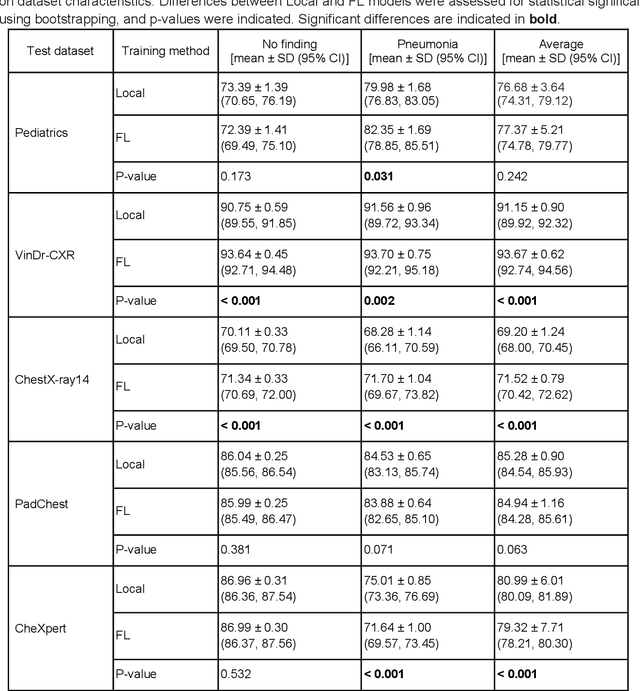
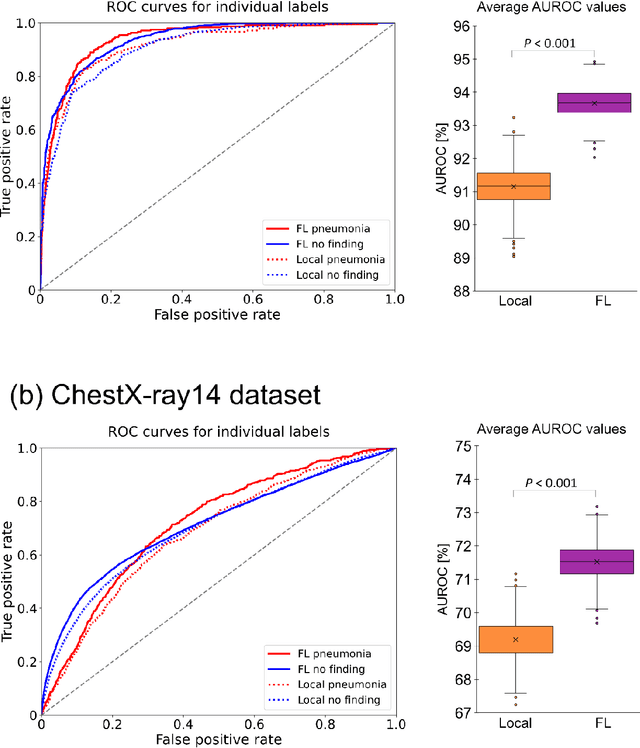
Reliable artificial intelligence (AI) models for medical image analysis often depend on large and diverse labeled datasets. Federated learning (FL) offers a decentralized and privacy-preserving approach to training but struggles in highly non-independent and identically distributed (non-IID) settings, where institutions with more representative data may experience degraded performance. Moreover, existing large-scale FL studies have been limited to adult datasets, neglecting the unique challenges posed by pediatric data, which introduces additional non-IID variability. To address these limitations, we analyzed n=398,523 adult chest radiographs from diverse institutions across multiple countries and n=9,125 pediatric images, leveraging transfer learning from general-purpose self-supervised image representations to classify pneumonia and cases with no abnormality. Using state-of-the-art vision transformers, we found that FL improved performance only for smaller adult datasets (P<0.001) but degraded performance for larger datasets (P<0.064) and pediatric cases (P=0.242). However, equipping FL with self-supervised weights significantly enhanced outcomes across pediatric cases (P=0.031) and most adult datasets (P<0.008), except the largest dataset (P=0.052). These findings underscore the potential of easily deployable general-purpose self-supervised image representations to address non-IID challenges in clinical FL applications and highlight their promise for enhancing patient outcomes and advancing pediatric healthcare, where data scarcity and variability remain persistent obstacles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge