Boosting Deep Hyperspectral Image Classification with Spectral Unmixing
Paper and Code
Apr 03, 2020
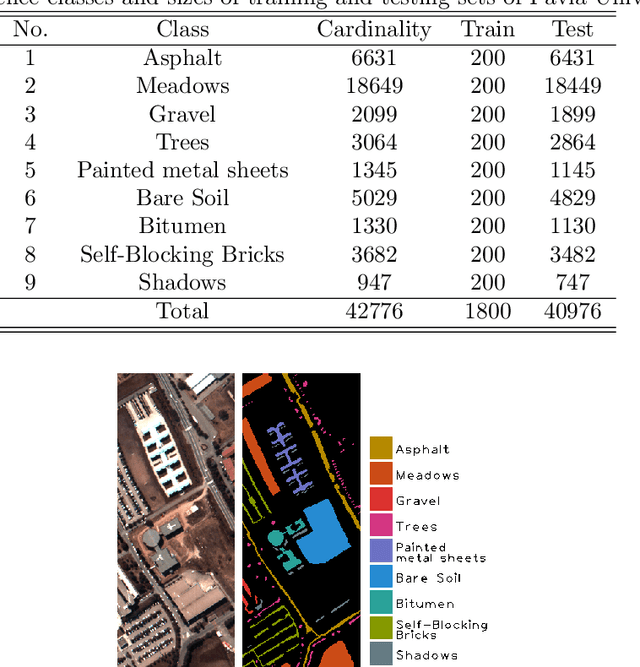
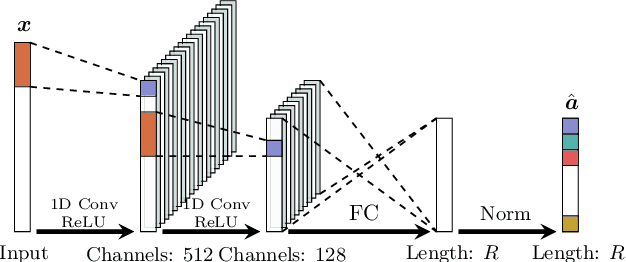
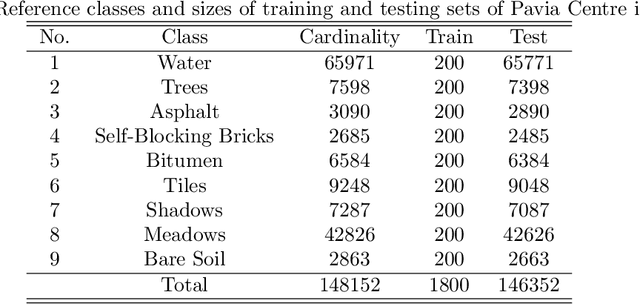
Recent advances in neural networks have made great progress in addressing the hyperspectral image (HSI) classification problem. However, the overfitting effect, which is mainly caused by complicated model structure and small training set, remains a major concern when applying neural networks to HSIs analysis. Reducing the complexity of the neural networks could prevent overfitting to some extent, but it declines the networks' ability to extract more abstract features. Enlarging the training set is also difficult. To tackle the overfitting problem, we propose an abundance-based multi-HSI classification method. By applying an autoencoder-based spectral unmixing technique, different HSIs are firstly converted from the spectral domain to the abundance domain. After that, the abundance representations from multiple HSIs are collected to form an enlarged dataset. Lastly, a simple classifier is trained, which makes predictions over all the involved datasets. Taking advantage of the spectral unmixing, transforming the spectral features to the abundance features significantly simplifies the classification tasks. This enables the use of a simple network as the classifier, thus alleviating the overfitting effect. Moreover, as much dataset-specific information is eliminated by the spectral unmixing, a compatible classifier suitable for different HSIs is trained. A several times enlarged training set is constructed by assembling the abundances from different HSIs. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by the ablation study and the comparative experiments. On four datasets, the proposed method provides comparable results with two state-of-the-art methods, but using a much simpler model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge