Black-Box Saliency Map Generation Using Bayesian Optimisation
Paper and Code
Jan 30, 2020
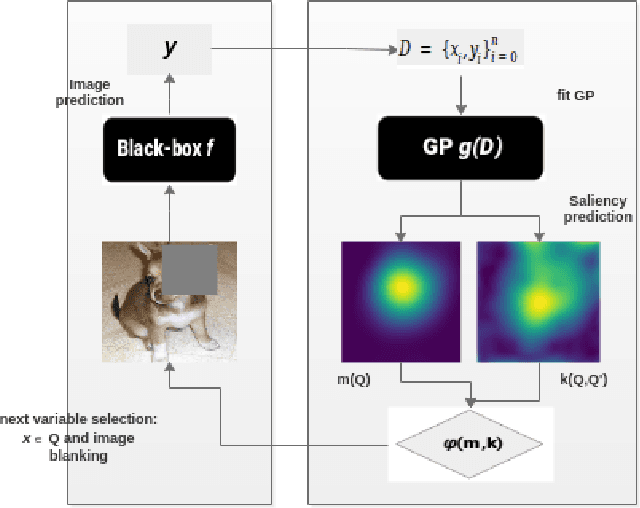
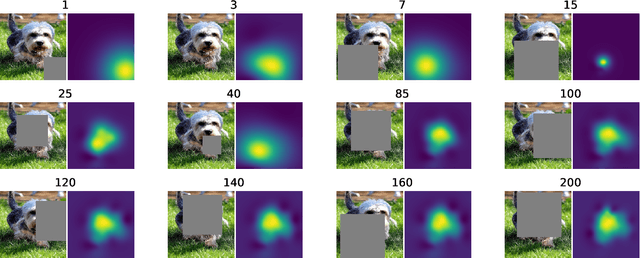
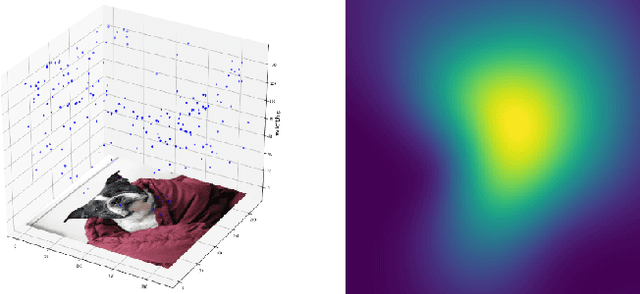
Saliency maps are often used in computer vision to provide intuitive interpretations of what input regions a model has used to produce a specific prediction. A number of approaches to saliency map generation are available, but most require access to model parameters. This work proposes an approach for saliency map generation for black-box models, where no access to model parameters is available, using a Bayesian optimisation sampling method. The approach aims to find the global salient image region responsible for a particular (black-box) model's prediction. This is achieved by a sampling-based approach to model perturbations that seeks to localise salient regions of an image to the black-box model. Results show that the proposed approach to saliency map generation outperforms grid-based perturbation approaches, and performs similarly to gradient-based approaches which require access to model parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge